The shift toward cloud computing is transforming how businesses operate in today's digital economy. No longer reliant solely on in-house servers or physical storage, companies are embracing the cloud to streamline operations, enhance flexibility, and reduce costs. Cloud technology allows businesses to store data, run applications, and collaborate in real time from virtually anywhere with an internet connection.
This shift is driven by several factors: the rise of remote work, the need for scalable solutions, and increasing pressure to remain competitive in a fast-moving market. Small startups and large enterprises alike are considering or already adopting cloud-based infrastructure. But as with any transformative change, the decision to move your business to the cloud comes with both advantages and challenges.
In this article, we'll explore the key benefits and drawbacks of cloud migration, helping you make a well-informed choice. Whether you're planning a full migration or adopting a hybrid approach, understanding the full scope of what cloud computing offers - and demands - is essential for future-proofing your business.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services - like storage, servers, databases, software, and networking - over the internet instead of relying on local servers or personal devices. This technology allows businesses to access and manage their data and applications from anywhere, at any time, using any internet-enabled device.
There are three main service models of cloud computing:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Access software applications over the internet (e.g., Google Workspace, Dropbox).
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Rent computing infrastructure like servers and storage (e.g., Amazon Web Services).
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure (e.g., Heroku, Microsoft Azure).
And four deployment models:
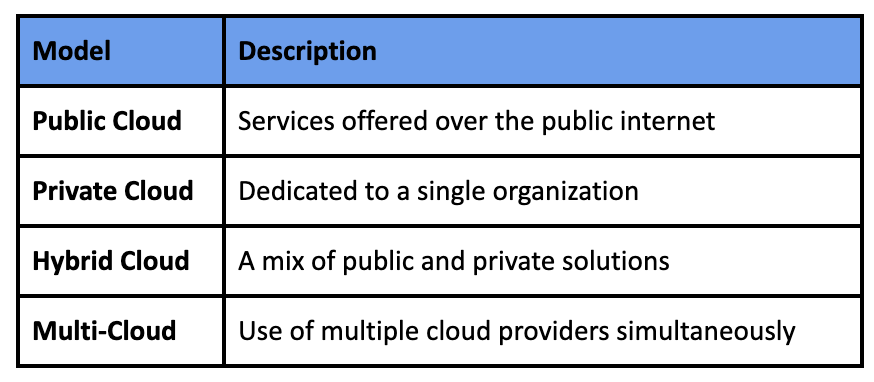
Understanding these basics is crucial before evaluating the pros and cons of cloud migration.
Why Businesses Are Moving to the Cloud
Businesses are increasingly adopting cloud computing due to its ability to simplify operations, cut costs, and enhance agility in a competitive market. The shift isn't just about storing files online - it's about embracing a modern way of running and scaling a business.
Here's why cloud adoption is on the rise:
- Cost Savings: Reduces upfront investments in hardware and IT infrastructure.
- Scalability: Quickly scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Remote Access: Enable employees to work from anywhere with real-time collaboration tools.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud providers manage software and security updates.
- Faster Deployment: New tools and apps can be launched without long installation times.
For startups, cloud platforms provide enterprise-level technology without the heavy price tag. For large enterprises, they offer flexibility and innovation at scale. The combination of these benefits creates a powerful incentive for businesses to rethink their traditional IT models and migrate to the cloud.
Pro #1: Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency stands out as one of the most persuasive reasons for moving a business to the cloud. Traditional IT infrastructure often demands substantial upfront investments in physical hardware, servers, software licenses, and dedicated IT staff for setup and ongoing maintenance. These expenses can quickly add up, especially for small or medium-sized businesses. "This makes cloud adoption especially appealing for growing companies, as it eliminates the need for heavy capital expenditure by offering a subscription-based model where businesses only pay for what they use," says Alex Vasylenko, Founder of Digital Business Card.
This pay-as-you-go approach not only reduces waste but also provides predictable monthly expenses, making it easier for businesses to manage their budgets. Additionally, cloud providers take care of updates, system maintenance, and hardware upgrades, which further reduces internal labor costs and technical headaches. By shifting these responsibilities to the cloud, companies can redirect their financial and human resources toward strategic growth areas, making cost efficiency a compelling advantage of cloud adoption.
Pro #2: Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are two powerful benefits that cloud computing offers to businesses of all sizes. Traditional IT environments can be rigid and difficult to expand, often requiring physical hardware upgrades, long installation times, and significant downtime. In contrast, cloud platforms allow companies to scale their operations up or down in real time based on actual demand. "This means a business can quickly increase its computing resources during peak seasons and reduce them when they are no longer needed, without the burden of overcommitting to long-term infrastructure costs," says Beatus Hoang, Senior Growth Manager at Exploding Topics.
Flexibility also comes into play when businesses need to adapt to changing work environments. Whether a company is transitioning to remote work, launching a new product line, or expanding into new markets, cloud services provide the tools and infrastructure to respond swiftly and efficiently. This ability to adjust on demand gives businesses a competitive edge in a fast-paced, constantly evolving digital landscape.
Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way teams collaborate by breaking down traditional barriers to communication and productivity. In the past, collaboration often required all team members to be in the same physical location or to manually share files through email or USB drives. With cloud-based tools, employees can now access shared documents, applications, and data in real time from any location with an internet connection.
This enables seamless teamwork across departments, offices, and even countries. Cloud platforms also support version control, allowing multiple users to work on the same file simultaneously while automatically saving changes and tracking edits.
As a result, the risk of miscommunication or data loss is significantly reduced. Moreover, integrated communication tools such as chat, video conferencing, and task management apps further enhance collaboration and streamline project workflows. Overall, the cloud fosters a more connected, efficient, and agile working environment, which is especially valuable in today's increasingly remote and hybrid work culture.
Pro #4: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity and disaster recovery are critical considerations for any organization, and cloud computing offers strong support in both areas. In traditional IT setups, unexpected events like hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks can result in significant data loss and extended downtime, potentially crippling operations. However, cloud platforms are designed with built-in redundancies and automated backup systems that ensure data is regularly saved and easily recoverable. "If a disruption occurs, businesses can quickly restore their systems and resume operations with minimal delay," says Anna Zhang, Head of Marketing at U7BUY.
This resilience is possible because cloud data is stored across multiple, geographically dispersed servers rather than being tied to a single physical location. Additionally, many cloud providers offer advanced recovery options and real-time failover systems that automatically switch to backup resources if the primary system encounters issues. As a result, companies using the cloud are better equipped to maintain operational continuity and safeguard their critical information during unforeseen challenges.
Pro #5: Improved Security Features
Security is a major concern for businesses in the digital age, and cloud computing offers a range of advanced features that help protect sensitive data and systems. Leading cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures, often exceeding the capabilities of in-house IT departments. These include data encryption, multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and continuous monitoring.
One of the key advantages is that security updates and patches are managed centrally by the provider, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly without requiring manual intervention from the user. Additionally, cloud providers typically follow strict compliance standards, such as ISO certifications or industry-specific regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
This level of security not only helps in safeguarding data but also assists businesses in meeting legal and regulatory obligations. While no system is entirely immune to threats, the layered and proactive approach offered by cloud platforms significantly strengthens a business's overall security posture.
Con #1: Internet Dependency
One of the primary drawbacks of cloud computing is its complete reliance on a stable and fast internet connection. Since cloud services are delivered over the internet, any disruption in connectivity can result in a temporary loss of access to essential applications, files, and communication tools. This poses a serious challenge for businesses operating in areas with unreliable or limited internet infrastructure.
Even in well-connected regions, outages caused by service provider issues, weather conditions, or network congestion can halt operations unexpectedly. Furthermore, during high-traffic periods, slow internet speeds can affect performance, making cloud-based tools laggy and inefficient. For businesses where uptime and immediate access are critical, such as healthcare or financial services, this dependency can pose a substantial risk.
While some cloud platforms offer offline functionality for limited tasks, full capabilities are typically only available when online. Therefore, internet dependency remains a significant consideration when deciding to shift operations to the cloud.
Con #2: Data Privacy and Compliance Risks
Data privacy and regulatory compliance are critical concerns when moving a business to the cloud. When sensitive customer or business data is stored on external servers managed by third-party providers, control over how that data is handled becomes more complex. "Different cloud providers store data in various geographic locations, each governed by its privacy laws and regulations. This can create confusion or even legal issues, especially for businesses operating in regions with strict data protection rules such as the European Union's GDPR or the United States' HIPAA requirements," says Xinrun Han, Marketing Manager at Mailgo. Misconfigurations, human error, or lack of visibility into how data is accessed and processed may lead to accidental exposure or breaches. Additionally, some industries require full transparency and control over data handling practices, which may not always be possible with certain cloud providers. While many cloud services offer compliance support, the responsibility still lies with the business to ensure its data management practices meet legal standards.
Con #3: Hidden or Unexpected Costs
While cloud computing is often praised for its cost efficiency, businesses can sometimes encounter hidden or unexpected expenses after migration. Many cloud services operate on a usage-based pricing model, which means costs can increase quickly as storage needs grow, more users are added, or advanced features are used.
Without careful monitoring, monthly bills can exceed initial expectations, especially when services are scaled rapidly or used inefficiently. Additionally, data transfer fees, integration with legacy systems, and custom configuration work can introduce extra charges that were not initially planned for.
There may also be costs associated with staff training, consulting, or reconfiguring business processes to fit cloud platforms. For businesses that require high levels of uptime or security, premium plans or add-ons might be necessary, further raising the total cost. Therefore, while the cloud can reduce some expenses, it is essential to conduct thorough cost analysis and ongoing usage tracking to avoid financial surprises.
Con #4: Limited Control and Customization
One significant drawback of cloud computing is the limited control businesses have over the underlying infrastructure and customization options. In a traditional on-premise environment, organizations can configure systems exactly to their needs, modify settings at the server level, and tailor every aspect of the software and hardware to suit their workflows. However, in a cloud environment, much of that control shifts to the service provider.
"Businesses must often operate within the constraints of standardized tools, configurations, and security protocols offered by the cloud vendor," explains Grant Aldrich, Founder & CEO of Preppy. This can be a challenge for companies with unique operational requirements, industry-specific software, or legacy systems that require deep customization.
Additionally, updates and changes are managed by the provider, meaning businesses must adapt to new features or interfaces, whether they are ready or not. This lack of flexibility can impact performance, user experience, and overall efficiency, especially for organizations that rely on specialized setups or highly tailored IT solutions.
Con #5: Security Vulnerabilities
Despite the advanced security features offered by most cloud providers, security vulnerabilities remain a notable concern when businesses transition to the cloud. Cloud environments are shared by multiple users and organizations, which can increase exposure to potential threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, or cyberattacks. While providers employ strict access controls and monitoring systems, human error - like misconfigured settings or weak passwords - can still lead to significant security incidents. In some cases, businesses mistakenly assume the cloud provider is solely responsible for protecting their data, overlooking the shared responsibility model where users must also enforce strong security practices.
Furthermore, sophisticated attackers often target cloud platforms specifically because they hold large volumes of valuable data. This makes cloud systems attractive targets and raises the stakes for businesses that store sensitive information. For industries dealing with intellectual property, financial data, or personal customer records, even a small vulnerability can result in major financial, legal, and reputational consequences.
Is the Cloud Right for Your Business?
While cloud computing offers many advantages, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. Before committing to cloud migration, businesses must assess their unique needs, industry requirements, and operational goals. Some organizations may benefit greatly from cloud flexibility, while others may find traditional infrastructure more reliable or cost-effective.
Key considerations before moving to the cloud:
- Business Size and Growth Plans: Cloud solutions are ideal for growing businesses that need scalable resources.
- Compliance Requirements: Highly regulated industries may need to ensure strict data control.
- IT Capabilities: Organizations with limited in-house IT support can benefit from cloud-managed services.
- Budget Flexibility: Subscription-based pricing works well for businesses that can tolerate variable costs.
- Data Sensitivity: Companies handling highly sensitive or proprietary data must carefully evaluate security models.
Taking the time to evaluate these factors helps ensure that the move to the cloud aligns with long-term strategic goals and avoids unnecessary challenges.
Conclusion: Weighing the Pros and Cons
The decision to move your business to the cloud is a strategic one that carries both exciting opportunities and important challenges. On the one hand, cloud computing offers compelling advantages such as cost efficiency, scalability, improved collaboration, stronger business continuity, and advanced security features. These benefits are particularly valuable in a fast-paced digital landscape where agility and responsiveness can define a business's success. The cloud enables organizations to operate more flexibly, serve customers more efficiently, and compete more effectively, regardless of their size or location.
However, these advantages do not come without trade-offs. Internet dependency, data privacy concerns, hidden costs, limited customization, and potential security vulnerabilities can pose real obstacles, particularly for businesses in sensitive industries or those with complex IT needs. Decision-makers need to look beyond marketing promises and thoroughly assess how cloud adoption fits into their specific operational environment and long-term goals.
Rather than approaching it as an all-or-nothing move, many businesses opt for a hybrid or phased migration, combining cloud benefits with existing infrastructure. This measured approach allows companies to test performance, monitor cost, and ensure compliance before committing fully. Ultimately, the best path forward is one that aligns with your business's values, capabilities, and vision for future growth.
Comments
Loading comments…