 Cover picture designed by the author
Cover picture designed by the author
Data is a key part of any mobile app. It gives meaning to a plain user interface. But storing, retrieving, and maintaining the data is the real hurdle. The use of different ways of storage mechanisms (encrypted store, offline store, service-oriented store, auto-sync store) is essential to store various kinds of data that can uplift the whole process of mobile app development. Because every user interface and functionality of the app need diverse data storage mechanisms to make that app spontaneous. I have listed all the existing ways to store data that are used to leverage app usability.
Async Storage
AsyncStorage is an **unencrypted, asynchronous, persistent, key-value **storage system that can be accessed globally on the app.
On iOS, AsyncStorage is backed by native code that stores small values in a serialized dictionary and larger values in separate files. On Android, AsyncStorage will use either RocksDB or SQLite based on availability. AsyncStorage supports only 6 MB on Android and a limitless amount of data on iOS. If you are aiming to build a cross-platform app, 6MB is the limit.
The JavaScript code acts as an interface and provides clean promise-based API methods, Error objects, and non-multi functions.
The ideal place to store common data of user, app-logic and others. GitHub - react-native-async-storage/async-storage: An asynchronous, persistent, key-value storage… *An asynchronous, unencrypted, persistent, key-value storage system for React Native. Head over to documentation to…*github.com
Secure Storage
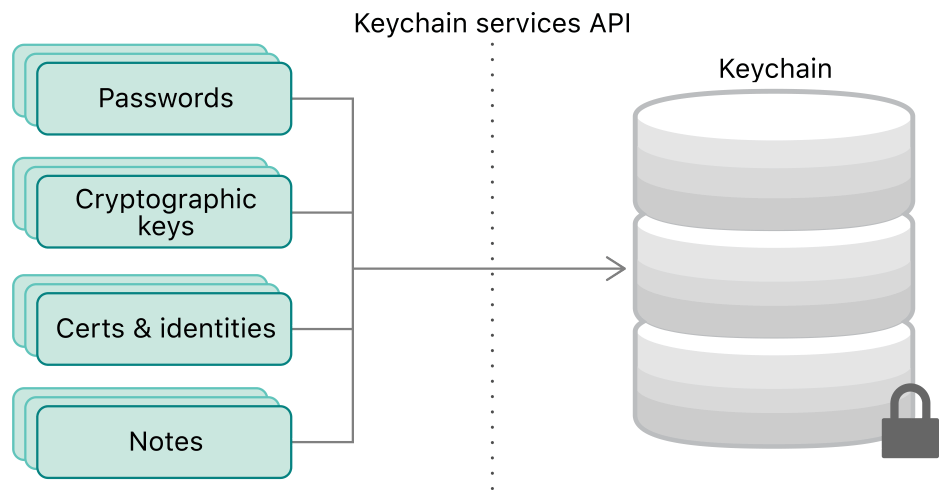
Secure storage helps to store encrypted data. React Native does not come bundled with any way of storing sensitive data. However, there are pre-existing solutions for Android and iOS platforms.
 Picture from iOS developer documentation
Picture from iOS developer documentation
On iOS, Keychain Services allows to securely store small chunks of sensitive info of the app. On Android, Shared Preference is the equivalent of a persistent key-value data store used for secure storage. Data in Shared Preferences is not encrypted by default, but Encrypted Shared Preferences wrap the Shared Preferences class for Android, and automatically encrypts keys and values.
But Android has another secure option than Shared Preferences called Android Keystore system that is used to store cryptographic keys in a container to make it more difficult to extract from the device. However, a branch of react-native-sensitive-info uses Android Keystore.
The ideal place to store certificates, tokens, passwords, and any other sensitive information that doesn’t belong in Async Storage.
GitHub - oblador/react-native-keychain: Keychain Access for React Native
GitHub - mCodex/react-native-sensitive-info: Save sensitive data into Android's Shared Preferences…
GitHub - emeraldsanto/react-native-encrypted-storage: React Native wrapper around…
SecureStore - Expo Documentation
MMKV Storage
MMKV is an efficient, small mobile key-value storage framework that was developed by Tencent to use in WeChat.
MMKV uses mmap to keep memory synced with files, and protobuf to encode/decode values, making the most of Android to achieve the best efficiency performance. It supports concurrent read-read and read-write access between processes which allows multi-process concurrency**.** It is easy to keep up the data because of fully synchronous calls.
The ideal place to store common data of users, app-logic, and others. It is an alternative for Async Storage. GitHub - ammarahm-ed/react-native-mmkv-storage: An ultra fast (0.0002s read/write), small &… *An ultra fast (0.0002s read/write), small & encrypted mobile key-value storage framework for React Native written in…*github.com GitHub - mrousavy/react-native-mmkv: ⚡️ An extremely fast key/value storage library for React… *MMKV is an efficient, small mobile key-value storage framework developed by WeChat. See Tencent/MMKV for more…*github.com
SQLite Storage
SQLite is a C-language library that implements a small, fast, self-contained, high-reliability, full-featured, SQL database engine. It is the most used database engine. It is built into all mobile phones and most computers and comes bundled inside countless other apps that people use every day. The file format is stable, cross-platform, and backward compatible and the developers pledge to keep it that way.
The ideal place to store more data than Async, Secure, and MMKV storage and it can support offline app development.
GitHub - Nozbe/WatermelonDB: 🍉 Reactive & asynchronous database for powerful React and React…
GitHub - andpor/react-native-sqlite-storage: Full featured SQLite3 Native Plugin for React Native…
GitHub - craftzdog/react-native-sqlite-2: SQLite3 Native Plugin for React Native for iOS, Android…
GitHub - ospfranco/react-native-quick-sqlite: ⚡️ The fastest SQLite implementation for…
Database Services
There are different types of database services available to perform various functionalities of the data layer of the mobile apps by following different approaches. Those are listed here.
-
Firebase Firestore
-
Firebase Database
-
Firebase Storage
-
Realm by Mongo DB
-
Pouch DB
Firebase Firestore
Cloud Firestore is a NoSQL document database that lets you easily** store, sync, and query data** for the mobile and web apps at Google scale. Can easily structure the data with collections and documents and use the hierarchies to store and retrieve the data easily using expressive queries.
react-native-firebase/packages/firestore at master · invertase/react-native-firebase
Firebase Database
The Firebase Realtime Database is cloud-hosted. Data is** stored as JSON and synchronized in real-time** to every connected client. When you build cross-platform apps with our React Native SDK, all of the clients share one Realtime Database instance and automatically receive updates with the newest data.
react-native-firebase/packages/database at master · invertase/react-native-firebase
Firebase Storage
Cloud Storage for Firebase is the ideal place to** store images, audio, video, or other user-generated content in the cloud**. It is a powerful, simple, and cost-effective object storage service built for Google scale. The Firebase SDKs for Cloud Storage add Google security to file uploads and downloads for the apps, regardless of network quality.
react-native-firebase/packages/storage at master · invertase/react-native-firebase
Realm by Mongo DB
Realm is a mobile database that runs directly inside phones, tablets, or wearables. Data is directly exposed as objects and queryable via code, removing the need for ORM. It supports relationships, generics, and vectorization. It is comparatively faster than raw SQLite and an alternative to SQLite & key-value stores. Realm’s local database persists data on-disk, so apps work offline too.
GitHub - realm/realm-js: Realm is a mobile database: an alternative to SQLite & key-value stores
Pouch DB
PouchDB is a pocket-sized database that enables apps to store data locally while offline, then synchronize it with CouchDB and compatible servers when the app is back online, keeping the user’s data in sync no matter where they next log in. Actually, PouchDB was designed for the web only. But now developer communities have created third-party libraries to support it on React Native too.
GitHub - seigel/pouchdb-react-native: Pouchdb with async storage
GitHub - craftzdog/pouchdb-react-native: - PouchDB is a pocket-sized database, with some patches…
Conclusion
Try out these data storage libraries to enhance the data storing and retrieving functionality in the React Native app. I am sure these exciting storage options will be useful to carry out different data-oriented tasks to create a full-fledged mobile app.
Thank you for reading the article.
Check this out👇
5 Useful User Interface Libraries for React Native Developers
Comments
Loading comments…