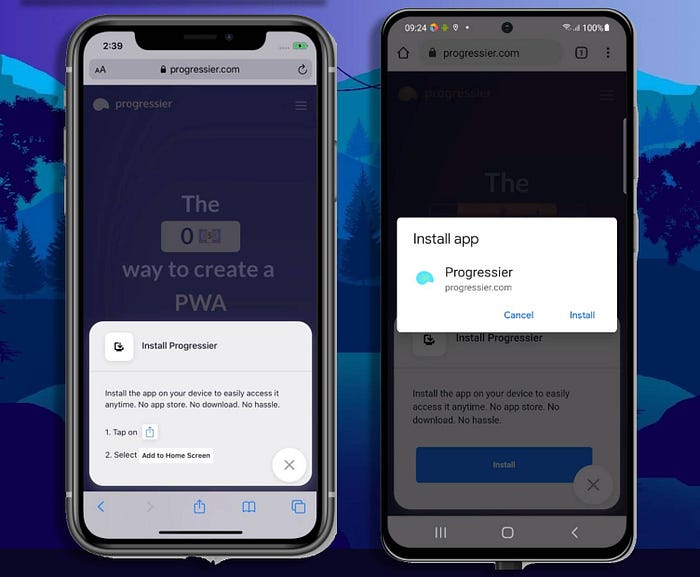
PWA installation on iOS (left) and Android (right)
One of Google’s best resources about PWA development is How to provide your own in-app install experience. Among other things, it explains in great detail how to create an install button and how to detect when a PWA has been installed. It works great… on Chrome.
What does it take to make a browser-agnostic install button?
It wouldn’t be fair to expect Google to write documentation for other browsers. No problem. But since the whole point of PWAs is that they work everywhere, an install button should by definition be browser-agnostic.
(Side note: With Progressier, creating an install button is as simple as adding <button class="progressier-install-button"></button>in your code but if absolutely want to build the logic yourself, please read on. Spoiler alert: it’s not fun.)
Okay, so what do we want to build?
We want to create a button, which, when clicked, triggers the Add to Home Screen prompt.
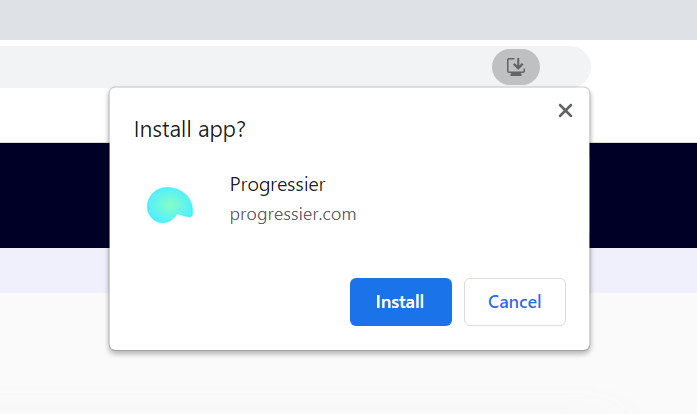
The “Add to Home Screen” prompt on desktop
On iOS, there is no prompt, so when clicked the button should display some instructions that explain how to add the app to their home screen manually.
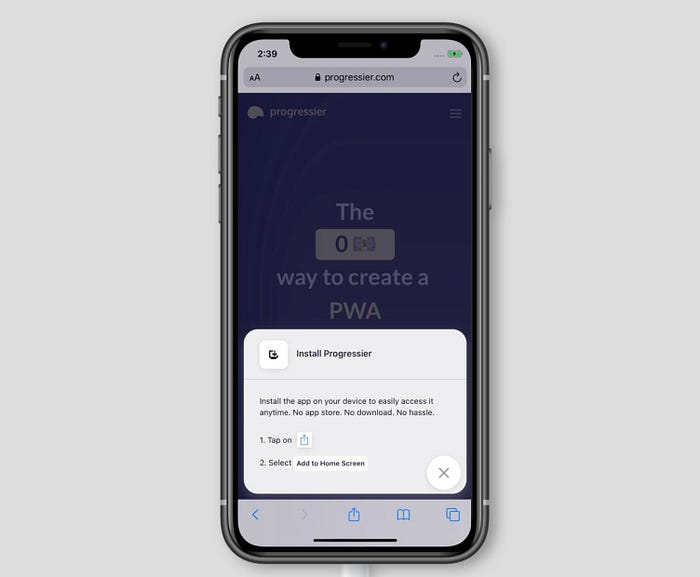
Instructions on how to install a PWA on iOS
On browsers that do no support the install functionality at all (e.g. Safari on Mac OS), the button should be disabled or hidden altogether. After the app has been installed, the button should either disappear or be disabled. We don’t want to ask our users to install our app after they’ve already done so.
So first, let’s create a button
let installButton = document.createElement('button');
Using the beforeinstallprompt event
For a domain to be installable, it must be secured by a SSL (i.e. starts with https://). It must also have a working service worker listening to the fetch event. And from August 2021, actually be available offline without shenanigans.
When all conditions are met, a beforeinstallprompt event is fired, telling the browser (and you) that the domain meets all conditions for installation. If you do nothing, Chrome will display what Google calls the mini-infobar.
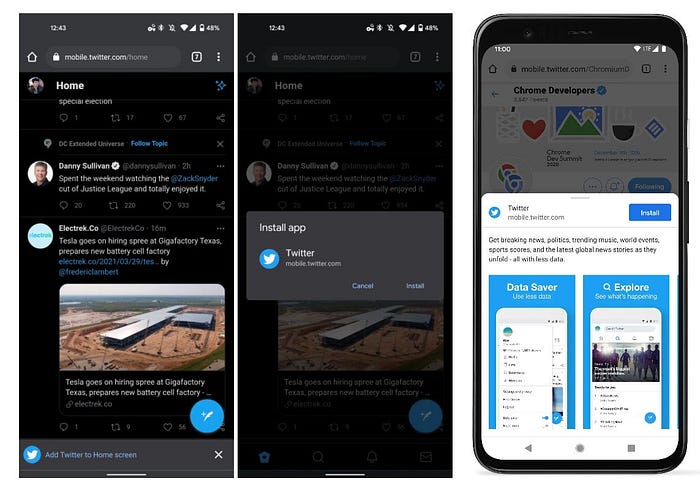
The “mini-infobar” (left), the “install prompt” (center), and the still-experimental “bottom sheet” (right).
Now, in our case, we need to catch the event and store it somewhere so we can invoke its prompt method when users click on our pretty installButton.
Cool. At this point, when users click on our button, it will prompt users to install the app.
Detecting app installation
Users can either click on “Install”. Or they can dismiss the prompt. This is how we can react to that choice.
There is another event we can listen to. It’s called appinstalled. It fires after the app has been added to our user’s home screen.
Simple enough. When the event is fired, we hide the installButton, so users can’t click it anymore. There is a little quirk though: the appinstalled event is never fired on Samsung Internet Browser (and possibly other browsers as well).
Is a PWA already installed? Or is it not installable at all?
Why do we care? Well, on devices that do not support the installation functionality, the right UX pattern is arguably to hide our installButton completely. Or show it but also indicate that the browser being used doesn’t support that function.
When a PWA has been installed, the best UX pattern is to disable the button and change its wording — from Install to Installed for example). Although hiding it completely is a decent option too.
Now, how do we tell if an app is installed (and therefore no longer installable) or if it simply not installable at all? In both cases, nothing will happen (no beforeinstallprompt or appinstalled events will be triggered).
So what we have to do is guess. Here are some methods that’ll help you do just that:
1. Feature detection
We can detect that a PWA is not installable by checking if the features required for that function are available. If not, we can be certain there’s no PWA functionality on that browser and hide our button altogether.
2. Standalone mode detection
If the app is open in its own window, we know for a fact that the app is already installed, and we can update our UI accordingly.
3. Cookies
Another valid option is to save a cookie on our user’s device whenever we’ve detected app installation. We want our installButton’s state to remain consistent across sessions. Note that we’ll likely also want to update the cookie if we detect a beforeinstallprompt event again. That means users have deleted our app — and therefore it has become installable again.
4. The getInstalledRelatedApps method
We can also use the getInstalledRelatedApps method to detect if our PWA has been installed.
5. iOS detection
iOS requires a different install promotion mechanism. But there’s no way to detect if a web page can use the iOS Add to Home Screen button. In order to show specific instructions on iOS only, we’ll have to figure out how to detect if a device is running iOS. There’s no future-proof way to do this, but here is one approach:
Conclusion
By making good use of all these workarounds, we can build a button that will show or hide depending on the browser’s compatibility and installation status. The biggest challenge with PWAs is also its greatest strength. Building an app that works everywhere also means you must make it work everywhere. And in some cases — like our install button — it can be rather tedious. Have you faced issues making a PWA install button? Leave a comment or email me at kevin@progressier.com.
Comments
Loading comments…