
1. What is KAG?
KAG is a logical reasoning and Q&A framework based on the OpenSPG engine and large language models, which is used to build logical reasoning and Q&A solutions for vertical domain knowledge bases. KAG can effectively overcome the ambiguity of traditional RAG vector similarity calculation and the noise problem of GraphRAG introduced by OpenIE. KAG supports logical reasoning and multi-hop fact Q&A, etc., and is significantly better than the current SOTA method.
The goal of KAG is to build a knowledge-enhanced LLM service framework in professional domains, supporting logical reasoning, factual Q&A, etc. KAG fully integrates the logical and factual characteristics of the KGs. Its core features include:
- Knowledge and Chunk Mutual Indexing structure to integrate more complete contextual text information
- Knowledge alignment using conceptual semantic reasoning to alleviate the noise problem caused by OpenIE
- Schema-constrained knowledge construction to support the representation and construction of domain expert knowledge
- Logical form-guided hybrid reasoning and retrieval to support logical reasoning and multi-hop reasoning Q&A
2. Core Features
2.1 Knowledge Representation
In the context of private knowledge bases, unstructured data, structured information, and business expert experience often coexist. KAG references the DIKW hierarchy to upgrade SPG to a version that is friendly to LLMs.
For unstructured data such as news, events, logs, and books, as well as structured data like transactions, statistics, and approvals, along with business experience and domain knowledge rules, KAG employs techniques such as layout analysis, knowledge extraction, property normalization, and semantic alignment to integrate raw business data and expert rules into a unified business knowledge graph.
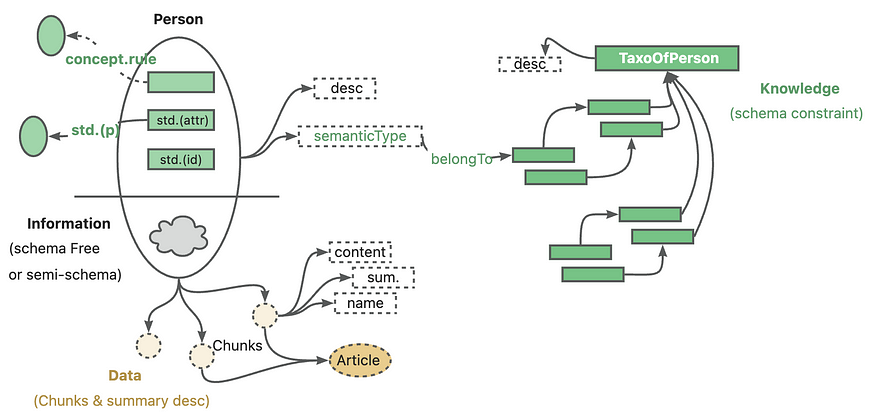
This makes it compatible with schema-free information extraction and schema-constrained expertise construction on the same knowledge type (e. G., entity type, event type), and supports the cross-index representation between the graph structure and the original text block.
This mutual index representation is helpful to the construction of inverted index based on graph structure, and promotes the unified representation and reasoning of logical forms.
2.2 Mixed Reasoning Guided by Logic Forms
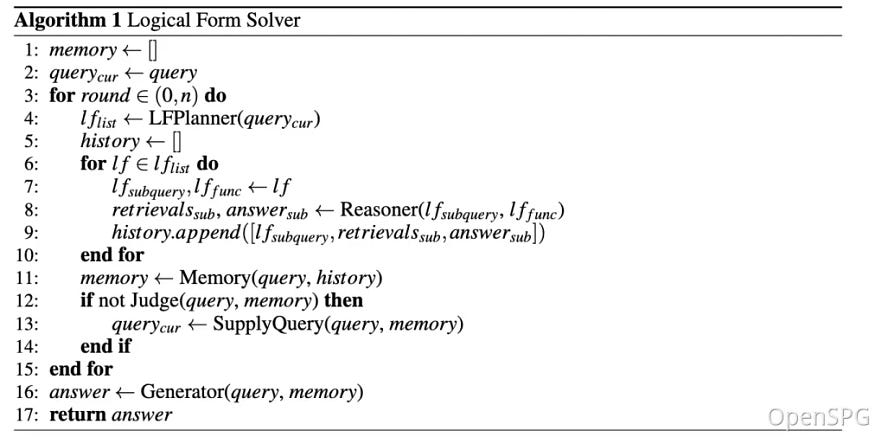
KAG proposes a logically formal guided hybrid solution and inference engine.
The engine includes three types of operators: planning, reasoning, and retrieval, which transform natural language problems into problem solving processes that combine language and notation.
In this process, each step can use different operators, such as exact match retrieval, text retrieval, numerical calculation or semantic reasoning, so as to realize the integration of four different problem solving processes: Retrieval, Knowledge Graph reasoning, language reasoning and numerical calculation.
Engine & Dependent Image Installation
- Recommend System Version:
macOS User:macOS Monterey 12.6 or later Linux User:CentOS 7 / Ubuntu 20.04 or later Windows User:Windows 10 LTSC 2021 or later- Software Requirements:
macOS / Linux User:Docker,Docker Compose Windows User:WSL 2 / Hyper-V,Docker,Docker Compose
Use the following commands to download the docker-compose.yml file and launch the services with Docker Compose.
# set the HOME environment variable (only Windows users need to execute this command)
# set HOME=%USERPROFILE%
curl -sSL [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenSPG/openspg/refs/heads/master/dev/release/docker-compose-west.yml](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenSPG/openspg/refs/heads/master/dev/release/docker-compose-west.yml) -o docker-compose-west.yml
docker compose -f docker-compose-west.yml up -d
4.1.2 Use the product
Navigate to the default url of the KAG product with your browser: http://127.0.0.1:8887
See KAG usage (product mode) for detailed introduction.
4.2 toolkit-based (for developers)
4.2.1 Engine & Dependent Image Installation
Refer to the 3.1 section to complete the installation of the engine & dependent image.
4.2.2 Installation of KAG
macOS / Linux developers
# Create conda env: conda create -n kag-demo python=3.10 && conda activate kag-demo
# Clone code: git clone [https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG.git](https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG.git)# Install KAG: cd KAG && pip install -e .
Windows developers
# Install the official Python 3.8.10 or later, install Git.
# Create and activate Python venv: py -m venv kag-demo && kag-demo\Scripts\activate# Clone code: git clone [https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG.git](https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG.git)# Install KAG: cd KAG && pip install -e .
Technical Architecture
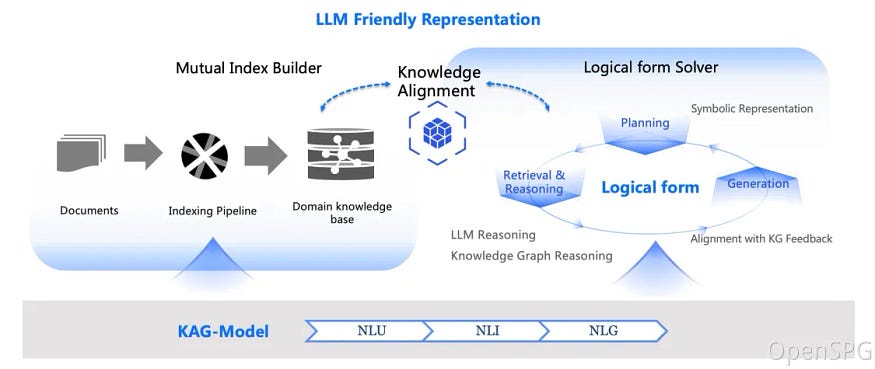
The KAG framework includes three parts: kg-builder, kg-solver, and kag-model. This release only involves the first two parts, kag-model will be gradually open source release in the future.
kg-builder implements a knowledge representation that is friendly to large-scale language models (LLM). Based on the hierarchical structure of DIKW (data, information, knowledge and wisdom), IT upgrades SPG knowledge representation ability, and is compatible with information extraction without schema constraints and professional knowledge construction with schema constraints on the same knowledge type (such as entity type and event type), it also supports the mutual index representation between the graph structure and the original text block, which supports the efficient retrieval of the reasoning question and answer stage.
kg-solver uses a logical symbol-guided hybrid solving and reasoning engine that includes three types of operators: planning, reasoning, and retrieval, to transform natural language problems into a problem-solving process that combines language and symbols. In this process, each step can use different operators, such as exact match retrieval, text retrieval, numerical calculation or semantic reasoning, so as to realize the integration of four different problem solving processes: Retrieval, Knowledge Graph reasoning, language reasoning and numerical calculation.
KAG usage (product mode)
This product provides a visual interface for OpenSPG-KAG, supporting users to build, ask and manage private domain knowledge bases on the page. At the same time, the modeling results can be viewed intuitively. When used in production mode, the KAG package python package is built into the openspg container, providing default building and reasoning question-answering capabilities. The calls to the generation model and representation model in the knowledge extraction and graph reasoning stages are all initiated from the openspg server container environment.
3.1 Create a knowledge base
3.1.1 Global configuration
●Common Configuration
user can custom database & vector model & prompt in common configuration
NOO4J:1/RELOASE-OPENSPG-NEO4J:7687
API_KEY
BAAI/BGE-M3
HTTPS://API.SILLICONFLOW.CN/V1
○database configuration
By default, the local openspg-neo4j graph storage database can be filled in. Example:
{
“database”:”neo4j”, # default datahbase name, which will be replaced by namespace of knowledge base
“uri”:”neo4j://release-openspg-neo4j:7687", # neo4j server address, which can be replaced by customized neo4j server which is accessbile
“user”:”neo4j”, # neo4j username, default to neo4j
“password”:”neo4j@openspg”, # neo4j password, default to neo4j@openspg
}
- vector configuration
{
“type”:”openai”, # KAG supports openai compatible interface of embedding service
“model”:”BAAI/bge-m3", # model name of embedding service
“base_url”:”[https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1](https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1)", # url of embedding service
“api_key”:”your api key”
}
- prompt
Required. Used to determine whether to use Chinese (zh) or English (en) when calling the model. Example:
{
“biz_scene”:”default”, # biz_scene for kag template
“language”:”en”, # en for english and zh for chinese
}
- Model configuration
KAG Supports Open-AI compatible generative Model APIs (chatgpt, deepseek, qwen2, etc.),provides maas, vllm, ollama and other modes, for details, refer to
Generate (chat) model configuration.
- maas
{
“model”: “deepseek-chat”,
“base_url”: “[https://api.deepseek.com](https://api.deepseek.com/)",
“api_key”: “deepseek api key”
}
- User Configuration
Account management can be done in User Configuration, including create/delete user, change password, etc.
New Knowledge Base
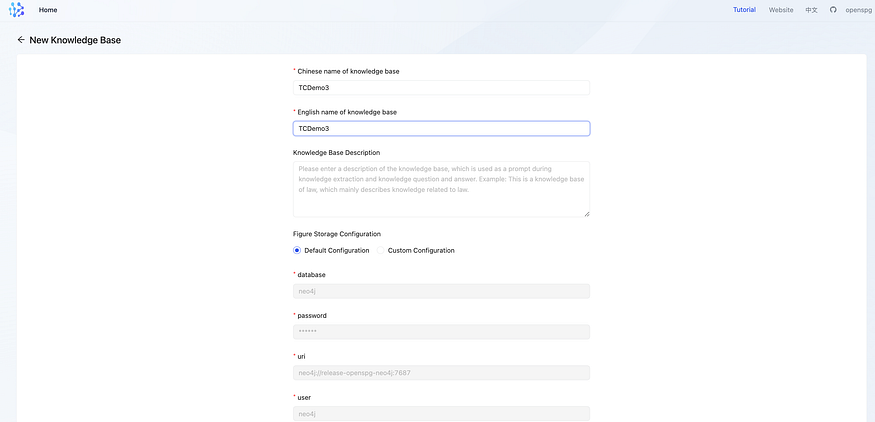
User can use global configuration for specific knowledge base, or customize a new configuration.
- namespace and graphStore configuration
we can use default configuration which was settled in global conf, default database name would be replaced by name of knowledge base.
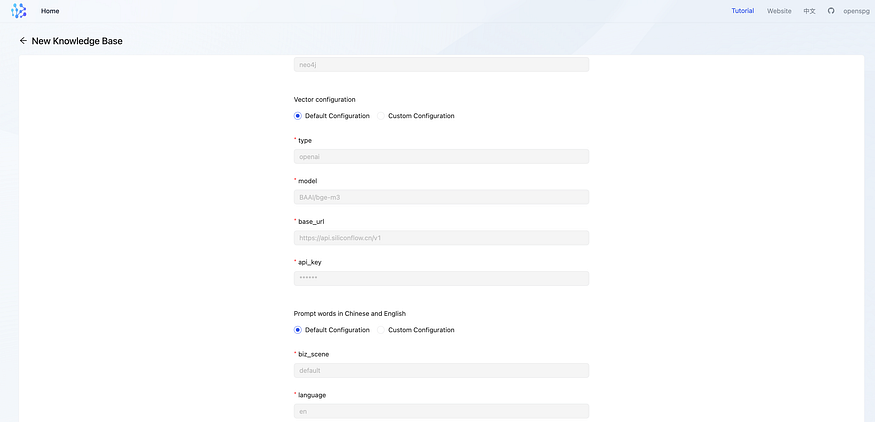
- vector configuration & prompts
we can use default configuration which was settled in global conf.
Special attention: embedding vectors generated by different representation models cannot be mixed even if they have the same dimensions; Therefore, in the knowledge base configuration, the configuration related to the representation model cannot be modified once it is set.
3.2 Import documents
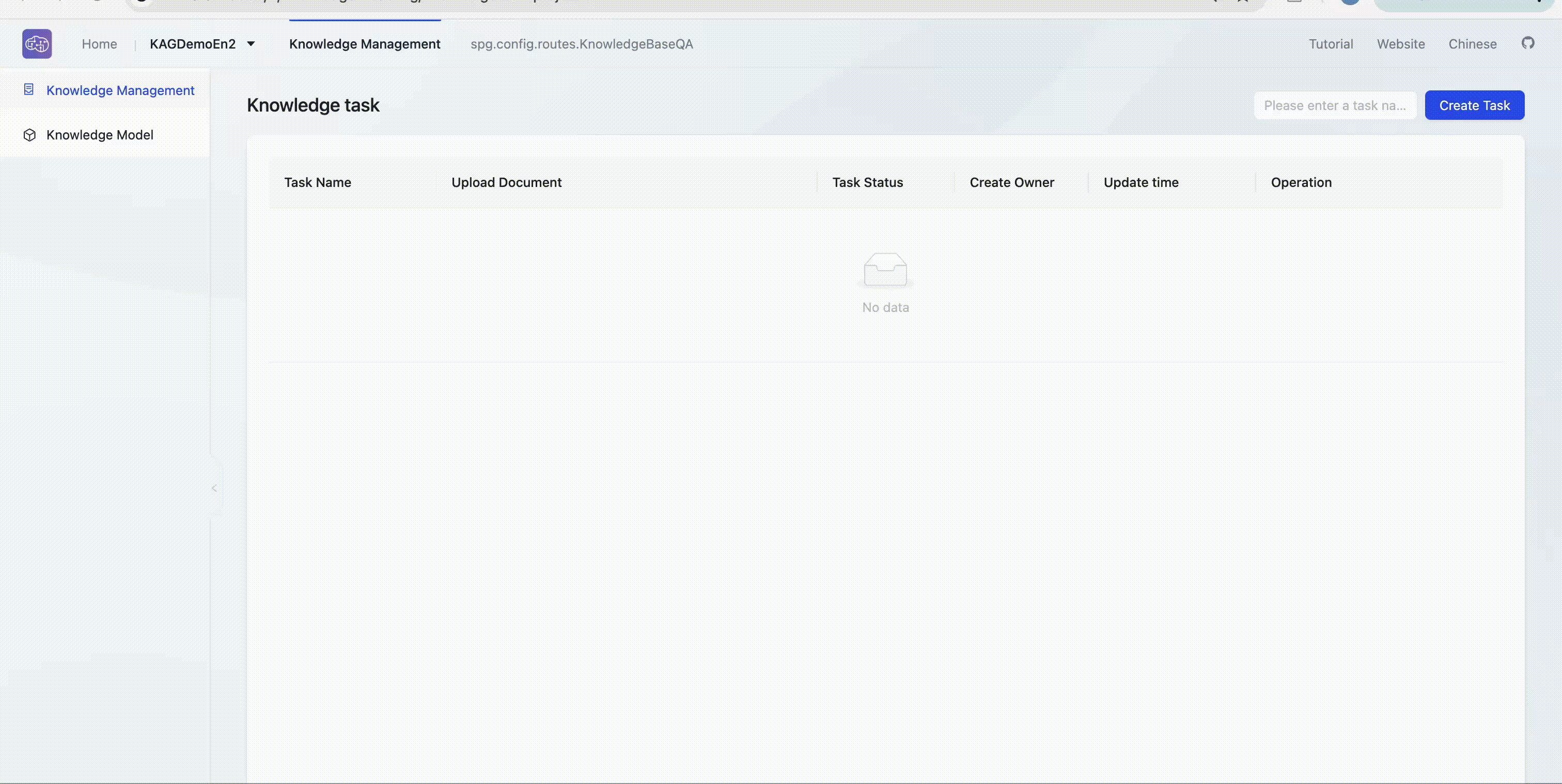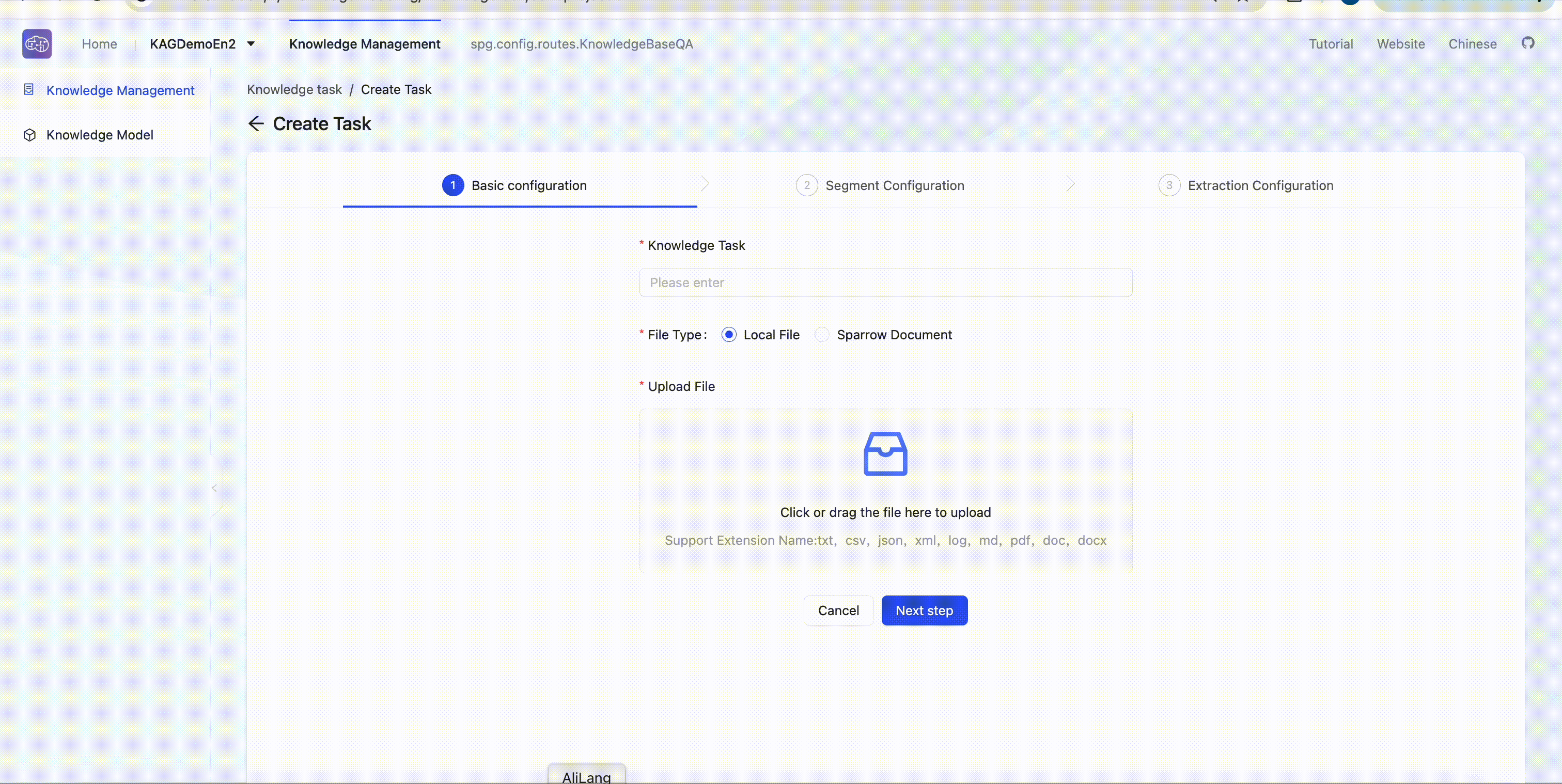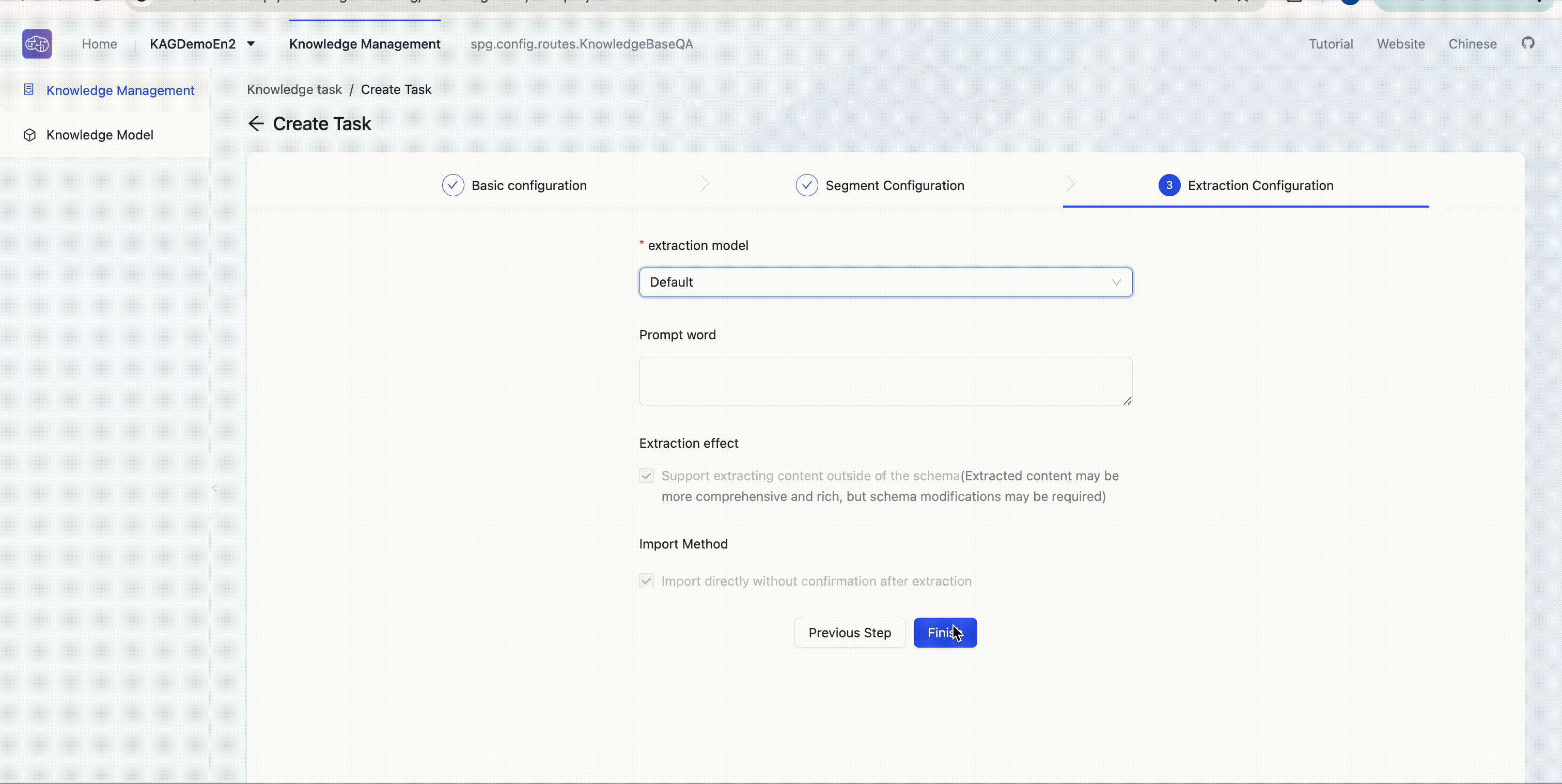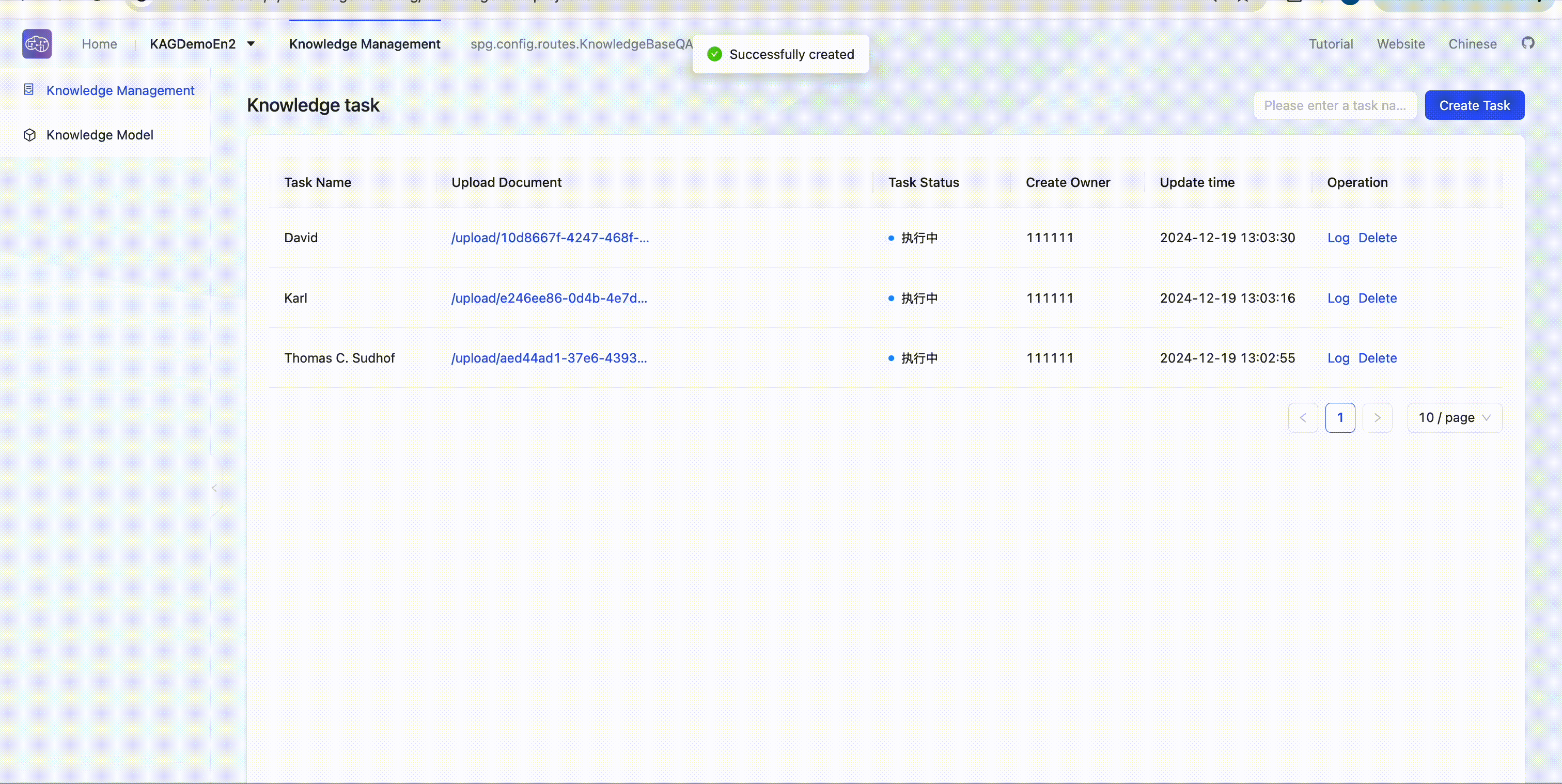
Create a build task
Enter the knowledge base Build => Create task to initiate knowledge building tasks. Users can download sample files 📎David Eagleman.txt 📎Karl Deisseroth.txt 📎Thomas C. Sudhof.txt for multi-hop Q&A tasks testing.
Check knowledge extraction Results
Users can view the graph data by clicking on the [Knowledge Exploration] menu on the product side.
Users can refer to Knowledge Exploration doc for detail.
中文
TUTORIAL
KNOWLEDGE BASE BULID
WEBSITE
TCDEMO1
CONFIGURATION
OPONSPG
KNOWLEDGE BASE BULID
KNOWLEDGE EXPLORATION
KNOWLEDGE MODEL
NAME OF KNOWLEDGE:
TYPE OF KNOWLEDGE:ALL
RESET
THOMAS C SUDHOF
A KNOWLEDGE EXPLORATION
FILTER
CAN BE FILTERED BY KNOWLED…
KNOWLEDGE LIST 6
TYPENAME
THOMAS C. SUDHEF THOMAS C….
C89953D2415051A6A007EB3…
THOMAS C.SUDHOF
TCDEMO1.CHUNK
THOMAS CHRISTIAN SUDHOF IS A
TCDEMO1.PERSON
THOMAS C SUDHOF
BLOCHEMIST
THOMAS C SUDHOF
THE BIRTH DATE OF THOMAS C.S…
TCDEMO1.DATE
BIRTH DATE
DECEMBER 22 1955
THOMAS C.SUDHOF
THOMAS C.SUDHOF
THOMAS CHRISTIAN S DHOF
TCDEMO1.PERSON
THOMAS CHRISTIAN S DHOF
BIOCHEMIST
SUDHOF S RESEARCH
KNOWLEDGE BASE BULID
CONFIGURATION
THOMAS C SUDHOF
ROASONING Q&A
BASIC INFO
KNOWLEDGE BASE BULID
KNOWLEDGE EXPLORATION
ENTITY TYPE:人物(TCDEMO1.PERSON)
KNOWLEDGE MODEL
RETUM TO TABLE
STATIC PROPERTY
KNOWLEDGE EXPLORATION
BASIC PROPERTIES
ATTRIBUTE (CHI… ATTRIBUTE(EN…
实体主链
名称
THOMAS C SUDHOF
DESC
DECEMBOR&21956
巴路北京自由自由
3.3 Reasoning Questions and Answers
Enter the question Which Stanford University professor works on Alzheimer’s? and wait for the result to return.
TUTORIAL
WEBSITE
中文
REASONING Q&A
CONFIGURATION
OPENSPG
KNOWLEDGE BASE BULID
NEW QUERY DIALOG
X
SUB QUESTION 1
WHICH STANFORD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WOR…
问题描述
MY FAVORITE
HISTORY
WHICH STANFORD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WORKS ON ALZHEIMER’S?
WHICH STANFORD UNIVE
问题回答
SUB QUESTION 2
THE STANFORD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WHO WORKS ON ALZHEIMER’S IS
WHICH OF THESE PROFESSORS WORK ON ALZH…
WHY?
THE EVIDENCE MEMORY EXPLICITLY STATES THAT THOMAS C.SUDHOF IS
A STANFARD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WHO WORKS ON ALZHEIMER’S.IT
DESCRIBES HIM AS A RENOWNED GERMAN-AMERICAN BIOCHEMIST
WITH APPOINTMENTS IN MULTIPLE DEPARTMENTS AT STANFORD’S SCHOOL
OF MEDICINE. HIS RESEARCH HAS SIGNIFICANTLY ADVANCED THE
WHICH STANFORD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WOR…
UNDERSTANDING OF ALZHEIMER’S,AND HE CONTINUES TO WORK ON
RE LATED RESEARCH AT THE HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INSTITUTE.THIS
井
MAKES HIM THE KEY FIGURE IN ALZHEIMER’S RESEARCH AT STANFORD
R
UNIVERSITY
O
QUESTION ANSWER
QUESTION:WHICH STANFORD UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR WORKS ON ALZHEIMER’S?
4 KAG usage (developer mode)
In the context of private domain knowledge bases, the effectiveness of graph construction and reasoning-based question answering is closely tied to schema design, knowledge extraction prompts, the selection of representation models, question planning prompts, graph retrieval algorithms, and answer generation prompts. These customizations are not yet exposed on the product side, requiring users to leverage the KAG developer mode to implement their customizations.
When using the developer mode, users execute the KAG Python package code in their local environment. The OpenSPG server solely provides capabilities such as schema management, reasoning execution, and graph database adaptation. Calls to generative models and representation models during the knowledge extraction and graph reasoning phases are initiated from the local environment.
Environment configuration
4.1.1 Pre-dependency
- OpenSPG-Server
KAG relies on OpenSPG-Server for metadata management and image storage services. Refer to the first and second parts of this document to complete the server deployment.
4.1.2 Virtual Environment Installation
# Install conda # conda installation :https://docs.anaconda.com/miniconda/
# Install python virtual env:
$ conda create -n kag-demo python=3.10 && conda activate kag-demo
Code Clone
# code clone:
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG.git
# KAG installation:
$ cd ./KAG && pip install -e .
# confirmation
$ knext — version
$ knext — help
Usage: knext [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]…
Options:
— version Show the version and exit.
— help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
project Project client.
reasoner Reasoner client.
schema Schema client.
thinker Thinker client.
Create a knowledge base
New Project
- enter the project examples Directory
$ cd kag/examples
- edit Project Configuration
$ vim ./example_config.yaml
# — — — — — — project configuration start — — — — — — — — #
openie_llm: &openie_llm
api_key: key
base_url: https://api.deepseek.com
model: deepseek-chat
type: maas
chat_llm: &chat_llm
api_key: key
base_url: https://api.deepseek.com
model: deepseek-chat
type: maas
vectorize_model: &vectorize_model
api_key: key
base_url: https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/
model: BAAI/bge-m3
type: openai
vector_dimensions: 1024
vectorizer: *vectorize_model
log:
level: INFO
project:
biz_scene: default
host_addr: http://127.0.0.1:8887
id: “1”
language: en
namespace: TwoWikiTest
# — — — — — — project configuration end — — — — — — — — #
# — — — — — — kag-builder configuration start — — — — — — — — #
kag_builder_pipeline:
chain:
type: unstructured_builder_chain # kag.builder.default_chain.DefaultUnstructuredBuilderChain
extractor:
type: schema_free_extractor # kag.builder.component.extractor.schema_free_extractor.SchemaFreeExtractor
llm: *openie_llm
ner_prompt:
type: default_ner # kag.builder.prompt.default.ner.OpenIENERPrompt
std_prompt:
type: default_std # kag.builder.prompt.default.std.OpenIEEntitystandardizationdPrompt
triple_prompt:
type: default_triple # kag.builder.prompt.default.triple.OpenIETriplePrompt
reader:
type: dict_reader # kag.builder.component.reader.dict_reader.DictReader
post_processor:
type: kag_post_processor # kag.builder.component.postprocessor.kag_postprocessor.KAGPostProcessor
similarity_threshold: 0.9
splitter:
type: length_splitter # kag.builder.component.splitter.length_splitter.LengthSplitter
split_length: 100000
window_length: 0
vectorizer:
type: batch_vectorizer # kag.builder.component.vectorizer.batch_vectorizer.BatchVectorizer
vectorize_model: *vectorize_model
writer:
type: kg_writer # kag.builder.component.writer.kg_writer.KGWriter
num_threads_per_chain: 1
num_chains: 16
scanner:
type: 2wiki_dataset_scanner # kag.builder.component.scanner.dataset_scanner.MusiqueCorpusScanner
# — — — — — — kag-builder configuration end — — — — — — — — #
# — — — — — — kag-solver configuration start — — — — — — — — #
search_api: &search_api
type: openspg_search_api #kag.solver.tools.search_api.impl.openspg_search_api.OpenSPGSearchAPI
graph_api: &graph_api
type: openspg_graph_api #kag.solver.tools.graph_api.impl.openspg_graph_api.OpenSPGGraphApi
exact_kg_retriever: &exact_kg_retriever
type: default_exact_kg_retriever # kag.solver.retriever.impl.default_exact_kg_retriever.DefaultExactKgRetriever
el_num: 5
llm_client: *chat_llm
search_api: *search_api
graph_api: *graph_api
fuzzy_kg_retriever: &fuzzy_kg_retriever
type: default_fuzzy_kg_retriever # kag.solver.retriever.impl.default_fuzzy_kg_retriever.DefaultFuzzyKgRetriever
el_num: 5
vectorize_model: *vectorize_model
llm_client: *chat_llm
search_api: *search_api
graph_api: *graph_api
chunk_retriever: &chunk_retriever
type: default_chunk_retriever # kag.solver.retriever.impl.default_fuzzy_kg_retriever.DefaultFuzzyKgRetriever
llm_client: *chat_llm
recall_num: 10
rerank_topk: 10
kag_solver_pipeline:
memory:
type: default_memory # kag.solver.implementation.default_memory.DefaultMemory
llm_client: *chat_llm
max_iterations: 3
reasoner:
type: default_reasoner # kag.solver.implementation.default_reasoner.DefaultReasoner
llm_client: *chat_llm
lf_planner:
type: default_lf_planner # kag.solver.plan.default_lf_planner.DefaultLFPlanner
llm_client: *chat_llm
vectorize_model: *vectorize_model
lf_executor:
type: default_lf_executor # kag.solver.execute.default_lf_executor.DefaultLFExecutor
llm_client: *chat_llm
force_chunk_retriever: true
exact_kg_retriever: *exact_kg_retriever
fuzzy_kg_retriever: *fuzzy_kg_retriever
chunk_retriever: *chunk_retriever
merger:
type: default_lf_sub_query_res_merger # kag.solver.execute.default_sub_query_merger.DefaultLFSubQueryResMerger
vectorize_model: *vectorize_model
chunk_retriever: *chunk_retriever
generator:
type: default_generator # kag.solver.implementation.default_generator.DefaultGenerator
llm_client: *chat_llm
generate_prompt:
type: resp_simple # kag/examples/2wiki/solver/prompt/resp_generator.py
reflector:
type: default_reflector # kag.solver.implementation.default_reflector.DefaultReflector
llm_client: *chat_llm
# — — — — — — kag-solver configuration end — — — — — — — — #
- create Project (One-to-one mapping with the knowledge base in the product):
$ knext project create — config_path ./example_config.yaml
- directory Initialization
After creating a project, a directory with the same name as the namespace field in the project configuration (e.g., TwoWikiTest in the example) will be created under the kag/examples directory, and the KAG project code framework will be initialized.
Users can modify one or more of the following files to customize the business-specific knowledge graph construction and reasoning-based question answering.
TwoWikiTest
├── builder
│ ├── data
│ ├── indexer.py
│ └── prompt
│ ├── ner.py
│ ├── std.py
│ └── tri.py
├── kag_config.cfg
├── reasoner
├── schema
│ ├── TwoWikiTest.schema
└── solver
├── evaForHotpotqa.py
└── prompt
├── logic_form_plan.py
└── resp_generator.py
update the project (Optional)
If there are any configuration changes, you may refer to the content of this section to update the configuration on the server side.
- enter the project examples Directory
$ cd kag/examples/TwoWikiTest
- edit Project Configuration
Note: Due to the varying usage of different representation models, it is not recommended to update the vectorizer configuration after the project has been created. If there is a need to update the vectorizer configuration, it is advised to create a new project instead.
$ vim ./kag_config.yaml
Once again, please ensure that all api-key fields have been correctly filled in.
- run command:
$ knext project update — proj_path ./
Import documents
- Enter the project directory
$ cd kag/examples/TwoWikiTest
- Obtain the corpus file
The test corpus data for the 2wiki dataset is located at examples/2wiki/builder/data/2wiki_corpus.json, which contains 6,119 documents and 1,000 question-answer pairs. To quickly run through the entire process, there is also a 2wiki_sub_corpus.json file in the directory, which includes only 3 documents. We will use this smaller dataset as an example for experimentation.
Copy the corpus file to the corresponding directory in the TwoWikiTest project:
$ cp ../2wiki/builder/data/2wiki_sub_corpus.json builder/data/
edit schema(Optional)
- Submit the updated schema to SPG server
$ knext schema commit
- Execute the build task.
Define the build script in the builder/indexer.py file:
$ vim ./builder/indexer.py
import os
import logging
from kag.common.registry import import_modules_from_path
from kag.builder.runner import BuilderChainRunner
logger = logging.getLogger(name)
def buildKB(file_path):
from kag.common.conf import KAG_CONFIG
runner = BuilderChainRunner.from_config(KAG_CONFIG.all_config[“kag_builder_pipeline”])
runner.invoke(file_path)
logger.info(f”\n\nbuildKB successfully for {file_path}\n\n”)
if name == “main”:
import_modules_from_path(“.”)
dir_path = os.path.dirname(file)
# Set the file_path to the path of the previously prepared corpus file.
file_path = os.path.join(dir_path, “data/2wiki_sub_corpus.json”)
buildKB(file_path)
- Builder Chain running
Run theindexer.py script to complete the graph construction of unstructured data
$ cd builder
$ python ./indexer.py
Once the build script is launched, a checkpoint directory for the task will be generated under the current working directory(i.e., ./builder), recording the checkpoints and statistical information of the construction pipeline.
builder
├── ckpt
│ ├── chain
│ ├── extractor
│ ├── kag_checkpoint_0_1.ckpt
│ ├── postprocessor
│ ├── reader
│ └── splitter
├── data
│ ├── 2wiki_sub_corpus.json
├── indexer.py
Use the following command to view the statistical information of the extraction task, such as how many nodes/edges are extracted from each document:
$ less ckpt/kag_checkpoint_0_1.ckpt
Use the following command to check how many document entries have been successfully processed and written to the graph database:
$ wc -l ckpt/kag_checkpoint_0_1.ckpt
The KAG framework provides a checkpoint-based resumption feature. If the task is interrupted due to program errors or other external reasons (such as insufficient LLM balance), you can re-execute indexer.py. KAG will automatically detect the checkpoint files and reuse the existing results.
- Result Inspection
Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Enter the project directory
cd kag/examples/TwoWikiTest
- Edit the QA script
$ vim ./solver/qa.py
Paste the following content into qa.py.
import json
import logging
import os
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
from tqdm import tqdm
from kag.common.benchmarks.evaluate import Evaluate
from kag.solver.logic.solver_pipeline import SolverPipeline
from kag.common.conf import KAG_CONFIG
from kag.common.registry import import_modules_from_path
from kag.common.checkpointer import CheckpointerManager
logger = logging.getLogger(name)
class EvaFor2wiki:
“””
init for kag client
“””
def init(self):
pass
“””
qa from knowledge base,
“””
def qa(self, query):
resp = SolverPipeline.from_config(KAG_CONFIG.all_config[“kag_solver_pipeline”])
answer, traceLog = resp.run(query)
logger.info(f”\n\nso the answer for ‘{query}’ is: {answer}\n\n”)
return answer, traceLog
if name == “main”:
import_modules_from_path(“./prompt”)
evalObj = EvaFor2wiki()
evalObj.qa(“Which Stanford University professor works on Alzheimer’s?”)
Git hub link:https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG?tab=readme-ov-file
url:https://openspg.yuque.com/ndx6g9/docs_en/rs7gr8g4s538b1n7#cikso
Comments
Loading comments…