Image Credits: CNN
Tesla Autopilot is based on a suite of sensors and cameras, including cameras mounted on the front, sides, and rear of the vehicle, as well as ultrasonic sensors in the bumpers and radar in the front of the car. These sensors and cameras provide the car with 360-degree visibility and the ability to detect objects and other vehicles at close range and at high speed.
The information gathered by the sensors is processed by the vehicle’s onboard computer, which is powered by a powerful NVIDIA Drive AGX Pegasus AI computer. This computer runs Tesla’s proprietary Autopilot software, which is constantly being updated and improved with new features and capabilities.
The Autopilot software uses computer vision algorithms to analyze the data from the sensors and identify objects, road features, and other vehicles on the road. It then uses this information to make real-time driving decisions, such as accelerating, braking, and steering.
Tesla Autopilot uses a combination of computer vision algorithms to process the data from its sensors and cameras, and make real-time driving decisions. Some of the algorithms that are commonly used in the Tesla Autopilot system include:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These algorithms are used for image recognition and classification, and are designed to process and analyze large amounts of visual data in real time.
- Object Detection: Object detection algorithms are used to identify and track objects in the vehicle’s field of view, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs. These algorithms can be based on traditional computer vision techniques, such as HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients), or more advanced deep learning-based approaches, such as YOLO (You Only Look Once) and R-CNN (Regions with Convolutional Neural Network Features).
- Optical Flow: Optical flow algorithms are used to estimate the movement of objects in the vehicle’s field of view, which helps the system make decisions about how to control the vehicle. These algorithms are typically based on computer vision techniques such as Lucas-Kanade or Horn-Schunck.
- Lane Detection: Lane detection algorithms are used to identify and track the road lanes in the vehicle’s field of view. These algorithms can be based on computer vision techniques such as Hough transforms or more advanced deep learning-based approaches.
- Semantic Segmentation: Semantic segmentation algorithms are used to segment the image into different regions, each representing a different object or road feature. This information can then be used to make driving decisions, such as avoiding obstacles or following a specific lane.
These are just a few examples of the computer vision algorithms that are used in Tesla Autopilot. The exact combination of algorithms used will depend on the specific requirements of the system and the driving conditions, and Tesla is constantly improving and updating its algorithms to provide the best possible driving experience for its customers.
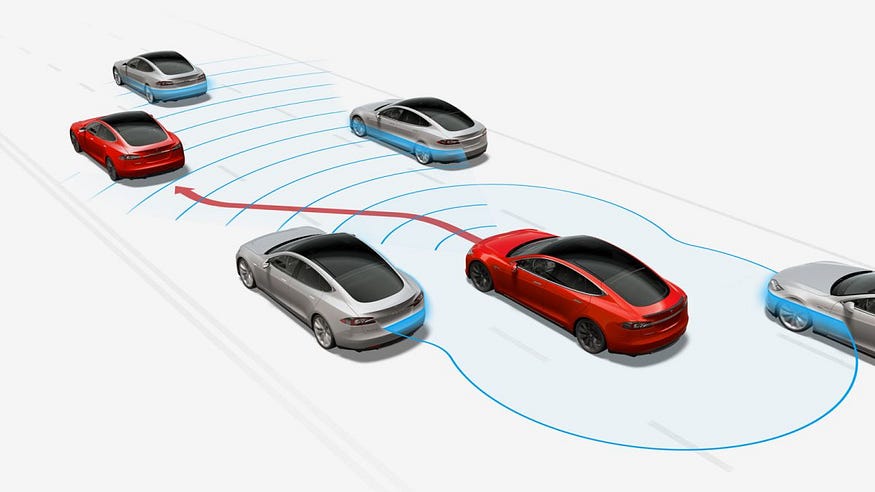
One of the key features of Tesla Autopilot is its ability to control the speed and direction of the car, keeping it centered in its lane and maintaining a safe following distance from the vehicle in front. This is achieved through the use of a combination of cameras and radar, as well as advanced algorithms that are designed to detect and respond to changing road conditions and traffic patterns.
Another important aspect of Tesla Autopilot is its ability to change lanes automatically. When the driver activates this feature, the system uses the cameras and sensors to assess the surrounding traffic and then make a decision about whether it is safe to change lanes. If it determines that the coast is clear, the car will smoothly and safely change lanes, returning control to the driver when the maneuver is complete.
In addition to these driving-assist features, Tesla Autopilot also includes a number of advanced safety technologies, such as automatic emergency braking, forward collision warning, and side collision warning. These systems use machine learning algorithms to analyze the data from the sensors and detect potential hazards, such as an impending collision, and provide an alert to the driver.
In conclusion, Tesla Autopilot is a highly sophisticated driving system that utilizes a suite of sensors and cameras, a powerful onboard computer, and advanced software algorithms to provide drivers with an unprecedented level of assistance and safety on the road.
Comments
Loading comments…