Knowledge Distillation
With the release of large models in the last few years, from GPT-3 to Megatron, I keep pondering how to experiment and use these models for a specific use case. These models are trained on massive corpuses of data (100+ GBs) with billions of parameters. Training or performing inference using such a model requires heavy computing and cost.
To overcome the above challenges, there are techniques developed to transfer the knowledge learnt by a larger model (teacher) and instil it into a smaller model (student).
Here the knowledge refers to parameters learnt during model training. This whole concept is called “Knowledge Distillation.” Knowledge distillation in machine learning refers to transferring knowledge from a teacher to a student model.

From Author
We can understand this teacher-student model as a teacher who supervises students to learn and perform in an exam. Though teachers have broad knowledge of the subject, they can narrow it down to the topics required by the student to excel in their exam. Now, with the understanding of what is knowledge distillation, we can talk about the different knowledge aspects in a teacher model that can be distilled to get a student model.
- Feature based knowledge distillation
- Response based Knowledge distillation
- Relation based knowledge distillation
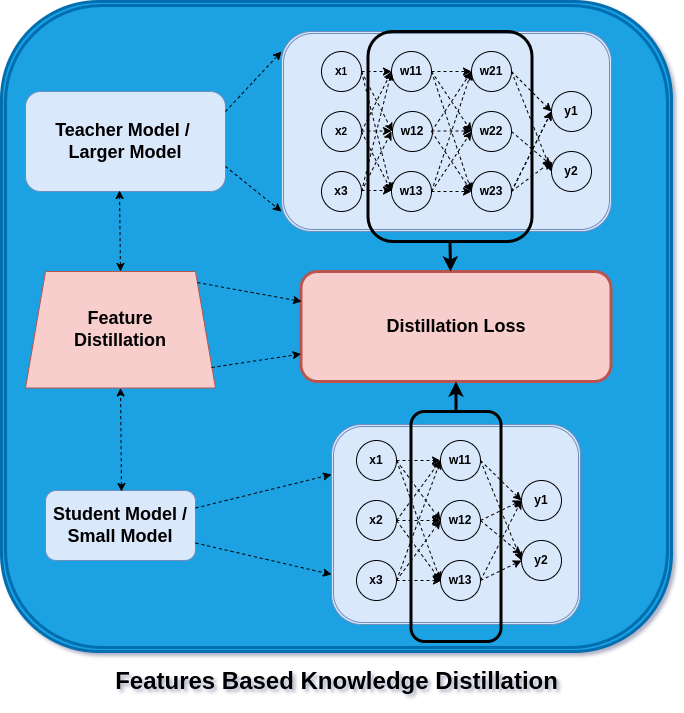
Feature Based Knowledge Distillation
In order to make the parameters (Ws) in the teacher model discriminate between the features of the different objects or classes, the parameters (Ws) in the training process are learned against a loss function.
From Author
For each class, there is a set of parameters (features) that are activated, which help in predicting that object or class. These same sets of feature activations are now learned using distillation loss when training a student model. The difference between a teacher’s and a student’s model’s activation of certain features is reduced with the aid of the loss function.
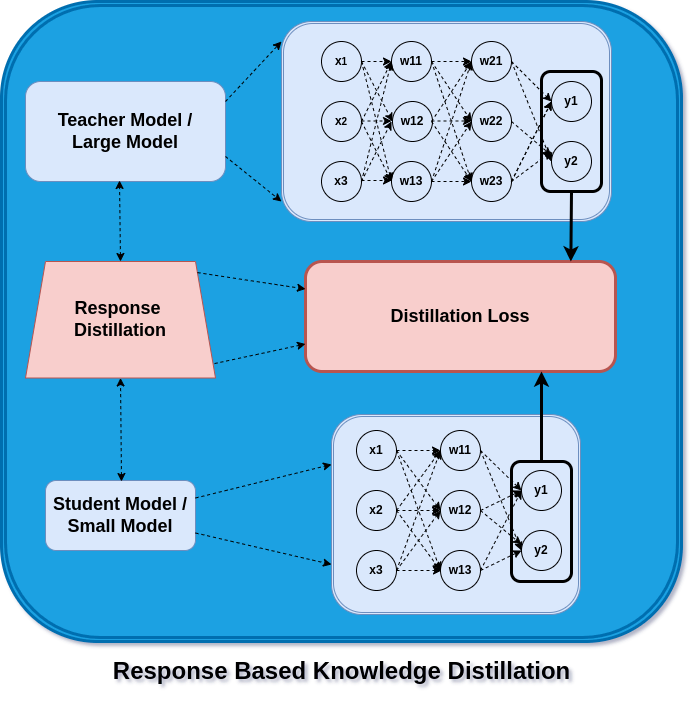
Response Based Knowledge Distillation
In feature distillation, the student model is optimized for feature activation against distillation loss. In response-based distillation, the student model makes use of the teacher model’s logits to enhance its own logits.
From Author
Here, the distillation loss aims to capture and reduce the variation in logits between the student and teacher models. The teacher model’s predictions are mimicked as the student model gains experience through training iterations.
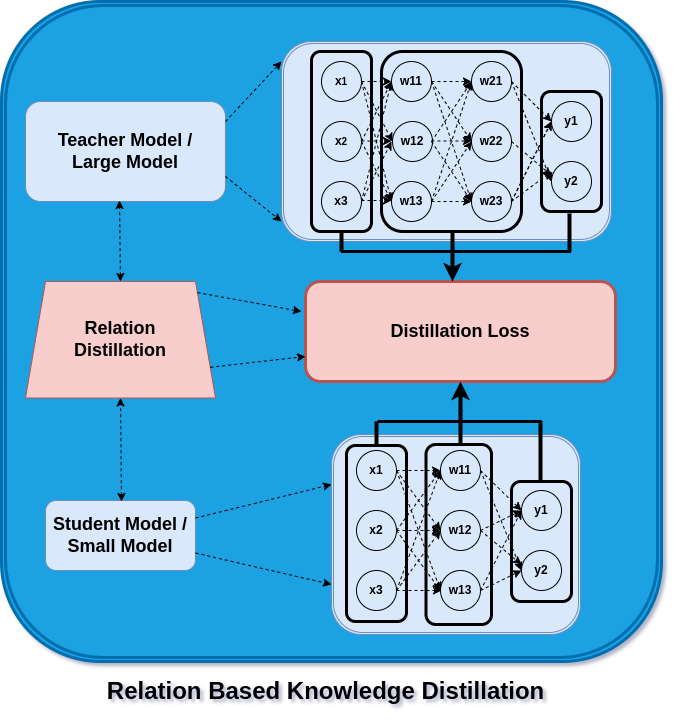
Relation Based Knowledge Distillation
From Author
In feature and response-based knowledge distillation, the outputs from feature activation and logits are used as a leverage to build the student model. However, in this case, we use the interrelationship of the layers as input with a hidden layer or a hidden layer with output as the source of learning for the student model. These relationships now consist of layers that can be thought of as probability distributions, similarity matrices, or feature embeddings. As a result, the student learns from the teacher’s model how to construct its embedding or distribution. In the next blog post, we’ll see how to train a knowledge distillation. Til then,
Comments
Loading comments…