
In this walkthrough I will be showing how to deploy a AWS Autoscaling group, a External Load Balancer and EC2s with Apache installed with Terraform. Your environment will need Terraform installed. I am using Cloud9 so Terraform is already preloaded.
Let’s get started
Step 1.
Make a directory for your Terraform files and then create a main.tf, variables.tf, output.tf, and a .sh file for the Apache server.
touch main.tf touch variables.tf touch output.tf touch yourbash.sh
Step 2.
Let’s initialize our directory
terraform init
Then write our code in the main.tf
First we will start with our VPC
resource "aws_vpc" "vpc" {
cidr_block = var.vpc_cidr
tags = {
Name = local.vpc_name
}
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "internet_gateway" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
tags = {
Name = local.internet_gateway_name
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {
count = 2
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet_cidr[count.index]
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
availability_zone = var.az_names[count.index]
tags = {
Name = join("-", [local.public_subnet_name, var.az_names[count.index]])
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {
count = 2
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
cidr_block = var.private_subnet_cidr[count.index]
availability_zone = var.az_names[count.index]
tags = {
Name = join("-", [local.private_subnet_name, var.az_names[count.index]])
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "public_route_table" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.internet_gateway.id
}
tags = {
Name = local.public_route_table_name
}
}
resource "aws_eip" "elastic_ip" {
tags = {
Name = local.elastic_ip_name
}
}
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "nat_gateway" {
allocation_id = aws_eip.elastic_ip.id
connectivity_type = "public"
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet[0].id
tags = {
Name = local.nat_gateway_name
}
depends_on = [aws_internet_gateway.internet_gateway]
}
resource "aws_route_table" "private_route_table" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
nat_gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.nat_gateway.id
}
tags = {
Name = local.private_route_table_name
}
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_rt_assoc" {
count = 2
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet[count.index].id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.public_route_table.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private_rt_assoc" {
count = 2
subnet_id = aws_subnet.private_subnet[count.index].id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.private_route_table.id
}
then we will create our Security Group Resources
# Security Group Resources
resource "aws_security_group" "alb_security_group" {
name = local.alb_security_group_name
description = "ALB Security Group"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
ingress {
description = "HTTP from Internet"
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = local.alb_security_group_name
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "asg_security_group" {
name = local.asg_security_group_name
description = "ASG Security Group"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
ingress {
description = "HTTP from ALB"
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.alb_security_group.id]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = local.asg_security_group_name
}
}
next lets create the launch template and the auto scaling group resources
# Launch Template and ASG Resources
resource "aws_launch_template" "launch_template" {
name = local.launch_template_name
image_id = var.ami
instance_type = var.instance_type
network_interfaces {
device_index = 0
security_groups = [aws_security_group.asg_security_group.id]
}
tag_specifications {
resource_type = "instance"
tags = {
Name = local.launch_template_ec2_name
}
}
user_data = filebase64("${path.module}/install-apache.sh")
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "auto_scaling_group" {
desired_capacity = var.desired_capacity
max_size = var.max_size
min_size = var.min_size
vpc_zone_identifier = [for i in aws_subnet.private_subnet[*] : i.id]
target_group_arns = [aws_lb_target_group.target_group.arn]
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.launch_template.id
version = aws_launch_template.launch_template.latest_version
}
}
next the Application Load Balancer resources
# Application Load Balancer Resources
resource "aws_lb" "alb" {
name = local.alb_name
internal = false
load_balancer_type = "application"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.alb_security_group.id]
subnets = [for i in aws_subnet.public_subnet : i.id]
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group" "target_group" {
name = local.target_group_name
port = 80
protocol = "HTTP"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
health_check {
path = "/"
matcher = 200
}
}
resource "aws_lb_listener" "alb_listener" {
load_balancer_arn = aws_lb.alb.arn
port = "80"
protocol = "HTTP"
default_action {
type = "forward"
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.target_group.arn
}
}
Those will all sit in our main.tf file….CTRL-S :)
Step 3.
Lets create the variable.tf file
This creates the local values
# Terraform Variables
# Local Values
locals {
vpc_name = "wk21-vnet"
internet_gateway_name = "wk21-internet-gateway"
public_subnet_name = "wk21-public-subnet"
private_subnet_name = "wk21-private-subnet"
public_route_table_name = "wk21-public-route-table"
private_route_table_name = "wk21-private-route-table"
elastic_ip_name = "wk21-nat-elastic-ip"
nat_gateway_name = "wk21-nat-gateway"
alb_security_group_name = "wk21-alb-security-group"
asg_security_group_name = "wk21-asg-security-group"
launch_template_name = "wk21-launch-template"
launch_template_ec2_name = "wk21-asg-ec2"
alb_name = "wk21-external-alb"
target_group_name = "wk21-alb-target-group"
}
next lets create the VPC variables
# VPC Variables
variable "vpc_cidr" {
description = "VPC cidr block"
type = string
default = "172.16.0.0/16"
}
variable "az_names" {
type = list(string)
default = ["us-east-1a", "us-east-1b"]
}
variable "public_subnet_cidr" {
description = "Public Subnet cidr block"
type = list(string)
default = ["172.16.0.0/24", "172.16.1.0/24"]
}
variable "private_subnet_cidr" {
description = "Private Subnet cidr block"
type = list(string)
default = ["172.16.10.0/24", "172.16.11.0/24"]
}
next lets create the launch template and auto scaling group variables
# Launch Template and ASG Variables
variable "ami" {
description = "ami id"
type = string
default = "ami-006dcf34c09e50022"
}
variable "aws_region" {
description = "AWS region name"
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "server_port" {
description = "The port the web server will be listening"
type = number
default = 8080
}
variable "elb_port" {
description = "The port the elb will be listening"
type = number
default = 80
}
variable "instance_type" {
description = "The type of EC2 Instances to run (e.g. t2.micro)"
type = string
default = "t2.micro"
}
variable "min_size" {
description = "The minimum number of EC2 Instances in the ASG"
type = number
default = 2
}
variable "max_size" {
description = "The maximum number of EC2 Instances in the ASG"
type = number
default = 5
}
variable "desired_capacity" {
description = "The desired number of EC2 Instances in the ASG"
type = number
default = 3
}
Step 4.
Lets create the output file. This will show us our load balancer public url
output "alb_public_url" {
description = "Public URL"
value = aws_lb.alb.dns_name
}
Step 5.
Lets create the bash script to install Apache
#!/bin/bash
# Install Apache on Ubuntu
sudo yum check-update
sudo yum -y update
# apache installation, enabling and status check
sudo yum -y install httpd
sudo systemctl start httpd
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl status httpd | grep Active
# firewall installation, start and status check
sudo yum install firewalld
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl status firewalld | grep Active
# adding http services
sudo firewall-cmd — permanent — add-service=http
# reloading the firewall
sudo firewall-cmd — reload
sudo cat > /var/www/html/index.html << EOF
<html>
<head>
<title> LUIT </title>
</head>
<body>
<p> TEAM BLACK TEAM
</body>
</html>
EOF
Step 6.
Now do a terraform plan
Everything should be good. Fix any errors that may pop up.
Now lets do a terraform apply -auto-approve

Notice the alb_public_url pops up :)
Step 7.
Lets verify that everything was created.
Instances are up

Subnets are up

Security groups are up

Auto scaling group was created with our specifications. Max 5, Min 2, Desired 3

Lets terminate a instance and see what happens

Our instance is now gone. Lets check the log in our ASG. Now we will see that a Ec2 was taken out of service in response to an EC2 health check indicating it has been terminate or stopped. AND that a new was deployed.

I terminated two instances for this so we were down toonly 1. But as you can see two more popped up.

Which indicates our ASG is working correctly.
Now lets check to see that our external application load balancer exists.

With two availability zones.
Lets the VPC.

VPC created.
Now lets take a look at our network

4 subnets, 2 public, 2 private, private and public routing table, IGW and NGW
Now lets make sure our apache server is doing its job.

And it is. Our External ALB is accessible from anywhere in world.
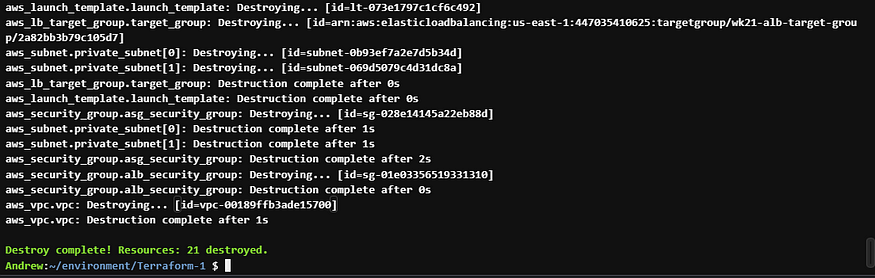
Now lets burn it down with terraform destroy -auto-approve
Be careful with -auto-approve. This bypasses the question do you really want to destroy this? In this case I use it because I know I don’t want what I just stood up.
And what we just deployed is now gone
And that is it. Thank you for sticking around I hope you enjoyed.