
If you have been in any interview process, then you know that during a technical interview process data structure questions must be asked. Actually, it's a very common and most important topic for any interview process. With DS questions an interviewer can judge a candidate's capability. In this article, I put together some basic DS questions asked for a JavaScript interview.
Array
1. Remove all even integers from an array
Input: [4, 1, 9, 10, 15, 22, 5, 14]
Output: [4, 10, 22, 14]
This problem has multiple solutions, It totally depends on a candidate. Here, I provide two solutions with an explanation.
Solution — 1
const inputData = [4, 1, 9, 10, 15, 22, 5, 14]
removeEvenNumbers (inputData) => {
let odds = []
for (let number of inputData) {
if (number % 2 != 0) odds.push(number)
}
return odds
}
console.log(removeEvenNumbers(inputData)))
// [4, 10, 22, 14]
In the above solution, we iterate through each element and check if it's even or odd. If it's odd then we push that into a separate array. So the time complexity of this problem is O(n)O(n).
Solution — 2
removeEvenNumbers(inputData) => {
return inputData.filter((number => (number % 2) != 0))
}
console.log(removeEvenNumbers(inputData))
This solution also iterates through all the elements and checks if it is even. If it is even, it filters out that element. I used filter to filter out array data, It just filters out data that returns a false value. It has the same time complexity.
2. Find all repeated numbers from an array
Input: [1,2,4,5,6,1,3,7,9,10]
Output: [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 3, 7, 9, 10]
const findUniqueNos = (inputData) => {
let uniqueNumbers = []
inputData.map(number => {
let counts = uniqueNumbers.filter(uniqueNo => uniqueNo == number)
if(counts.length != 1) uniqueNumbers.push(number)
})
return uniqueNumbers
}
console.log(findUniqueNos(inputData))
Simple? Yes, You need to loop through an array, and before that, you need to create one empty array and keep pushing a unique number into it. Just use filtering to identify if a number is already there or not.
Stack
1. Validate balanced parentheses
Write a function which takes only parentheses (curly {}, square [], or round ()). It should check that all parentheses in provided string is balanced or not. Simply it should check if there's an opening parentheses then it should have closing parentheses.
First input: {[({})]}
First output: true
Second input: {[({})}
Second output: false
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = []
this.top = null
}
getTop() {
if (this.items.length == 0)
return null
return this.top
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length == 0
}
size() {
return this.items.length
}
push(element) {
this.items.push(element)
this.top = element
}
pop() {
if (this.items.length != 0) {
if (this.items.length == 1) {
this.top = null
return this.items.pop()
} else {
this.top = this.items[this.items.length - 2]
return this.items.pop()
}
} else
return null
}
}
isBalancedParantheses(exp) => {
let myStack = new Stack()
// Loop through input string
for (let i = 0 i < exp.length i++) {
// Check for every closing parantheses if there's opeaning parantheses or not.
if (exp[i] == '}' || exp[i] == ')' || exp[i] == ']') {
if (myStack.isEmpty()) return false
let output = myStack.pop()
//If no opening parentheses for any closing one then immediatly return false
if (((exp[i] == "}") && (output != "{")) || ((exp[i] == ")") && (output != "(")) || ((exp[i] == "]") && (output != "["))) {
return false
}
} else {
//For each opening parentheses, push it into stack
myStack.push(exp[i])
}
}
//after traversal of input data, if there's any opening parentheses left in stack then also return false else return true at the end
if (myStack.isEmpty() == false) {
return false
}
return true
}
let firstInputData = "{[({})]}"
console.log(isBalancedParantheses(firstInputData))
secondInputData = "{[({})}"
console.log(isBalancedParantheses(secondInputData))
So at the beginning we loop through string and check character by character. There are two ways to identify unbalanced parentheses. First by stack value, second by top element of the stack. For that we need to check if stack is empty? OR Is top element on the stack is the right match? Any of these two condition gets true we immediately return false Opening paranthesis pushed into the stack, and if we got match then it will be popped. So you might wonder what's the time complexity of these code, since we iterate through only one time it's complexity will be O(n).
2. Write a function for converting numbers to base 2 and base 8
In this program you should write one function that will take integer value and one base value and then convert accordingly. Like for example, if an input is num = 14 and base = 2 then the result is 1110, num = 14, and base = 8 then the result is 16
Stack() => {
constructor() {
this.items = []
this.top = 0
}
push (element) => {
this.items[this.top++] = element
}
pop () => {
return this.items[--this.top]
}
length () => {
return this.top
}
}
convertBase(num, base) => {
let s = new Stack()
while( num > 0 ){
s.push(num % base)
num = Math.floor(num /= base)
}
let converted = ""
while (s.length() > 0) {
converted += s.pop()
}
return converted
}
let num = 14
let base = 2
console.log(convertBase(num, base))
In this program basically we push number into the stack after conversion and then pop one by one digit of a number and then return a whole number.
Queue
1. Print binary number up to N, where N can be any positive integer
In this problem, we need to write a program which will take integer number and generate binary numbers till the limit. Like is input number n = 3 then the result should be [1,10,11]
module.exports = class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = []
this.front = null
this.back = null
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length == 0
}
getFront() {
if (this.items.length != 0) {
return this.items[0]
} else
return null
}
size() {
return this.items.length
}
enqueue(element) {
this.items.push(element)
}
dequeue() {
if (this.items.length == 0) {
return null
} else {
return this.items.shift()
}
}
}
generateBinaryNumbers(n) => {
let result = []
let myQueue = new Queue()
let s1, s2
myQueue.enqueue("1")
for (let i = 0 i < n i++) {
result.push(myQueue.dequeue())
s1 = result[i] + "0"
s2 = result[i] + "1"
myQueue.enqueue(s1)
myQueue.enqueue(s2)
}
return result
}
console.log(generateBinaryNumbers(3))
For generating binary number, we need to append 0 and 1 to previous binary number, like from 1 we can generate 10 and 11 by appending 0 and 1. Once you generate a binary number then enqueue to a queue for generating next number by appending 0 and 1. The time complexity of given solution is in O(n)O(n) because same operation running n times.
2. Explain how the priority queue system works.
In this program first you need to create a queue and then implement priority queue. Let me explain with an example.
Patient(name, code) => {
this.name = name
this.code = code
}
Queue() => {
this.dataStore = []
enqueue(element) => {
this.dataStore.push(element)
}
dequeue() => {
let priority = this.dataStore[0].code
for (let i = 1; i < this.dataStore.length; ++i) {
if (this.dataStore[i].code < priority) {
priority = i
}
}
return this.dataStore.splice(priority,1)
}
front() => {
return this.dataStore[0]
}
back() => {
return this.dataStore[this.dataStore.length-1]
}
toString() => {
let retStr = ""
for (let i = 0; i < this.dataStore.length; ++i) {
retStr += this.dataStore[i].name + " code: " + this.dataStore[i].code + "\n"
}
return retStr
}
empty() => {
if (this.dataStore.length == 0) {
return true
}
else {
return false
}
}
let p = new Patient("Smith",5)
let ed = new Queue()
ed.enqueue(p)
p = new Patient("Jones", 4)
ed.enqueue(p)
p = new Patient("Fehrenbach", 6)
ed.enqueue(p)
p = new Patient("Brown", 1)
ed.enqueue(p)
p = new Patient("Ingram", 1)
ed.enqueue(p)
console.log(ed.toString())
let seen = ed.dequeue()
console.log("Patient being treated: " + seen[0].name)
console.log("Patients waiting to be seen: ")
console.log(ed.toString())
// another round
let seen = ed.dequeue()
console.log("Patient being treated: " + seen[0].name)
console.log("Patients waiting to be seen: ")
console.log(ed.toString())
let seen = ed.dequeue()
console.log("Patient being treated: " + seen[0].name)
console.log("Patients waiting to be seen: ")
console.log(ed.toString())
Generated output is like below:
Smith code: 5
Jones code: 4
Fehrenbach code: 6
Brown code: 1
Ingram code: 1
Patient being treated: Jones
Patients waiting to be seen:
Smith code: 5
Fehrenbach code: 6
Brown code: 1
Ingram code: 1
Patient being treated: Ingram
Patients waiting to be seen:
Smith code: 5
Fehrenbach code: 6
Brown code: 1
Patient being treated: Brown
Patients waiting to be seen:
Smith code: 5
Fehrenbach code: 6
As name suggest priority queue is used when you want to remove something from a queue based on priority. So, here I take an example of patient and it's visiting number. Basically it represent waiting room of any hospital. Here dequeue() function will remove the patient from the queue based on lowest priority after that toString() modifies the handled patient object.
Linked List
1. Write a program to reverse a linked list
Input: A linked list like this LinkedList = 0->1->2->3-4
Output: A reverse linked list LinkedList = 4->3->2->1->0
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data
this.nextElement = null
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
}
//Insertion At Head
insertAtHead(newData) {
let tempNode = new Node(newData)
tempNode.nextElement = this.head
this.head = tempNode
return this //returning the updated list
}
isEmpty() {
return (this.head == null)
}
to print the linked lis=> t
printList() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Empty List")
return false
} else {
let temp = this.head
while (temp != null) {
process.stdout.write(String(temp.data))
process.stdout.write(" -> ")
temp = temp.nextElement
}
console.log("null")
return true
}
}
getHead() {
return this.head
}
setHead(newHead) {
this.head = newHead
return this
}
getListStr() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Empty List")
return "null"
} else {
let st = ""
let temp = this.head
while (temp != null) {
st += String(temp.data)
st += " -> "
temp = temp.nextElement
}
st += "null"
return st
}
}
insertAtTail(newData) {
//Creating a new Node with data as newData
let node = new Node(newData)
//check for case when list is empty
if (this.isEmpty()) {
//Needs to Insert the new node at Head
this.head = node
return this
}
//Start from head
let currentNode = this.head
//Iterate to the last element
while (currentNode.nextElement != null) {
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement
}
//Make new node the nextElement of last node of list
currentNode.nextElement = node
return this
}
search(value) {
//Start from the first element
let currentNode = this.head
//Traverse the list until you find the value or reach the end
while (currentNode != null) {
if (currentNode.data == value) {
return true //value found
}
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement
}
return false //value not found
}
deleteAtHead() {
//if list is empty, do nothing
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return this
}
//Get the head and first element of the list
let firstElement = this.head
//If list is not empty, link head to the nextElement of firstElement
this.head = firstElement.nextElement
return this
}
deleteVal(value) {
let deleted = null //True or False
//Write code here
//if list is empty return false
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return false
}
//else get pointer to head
let currentNode = this.head
// if first node's is the node to be deleted, delete it and return true
if (currentNode.data == value) {
this.head = currentNode.nextElement
return true
}
// else traverse the list
while (currentNode.nextElement != null) {
// if a node whose next node has the value as data, is found, delete it from the list and return true
if (currentNode.nextElement.data == value) {
currentNode.nextElement = currentNode.nextElement.nextElement
return true
}
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement
}
//else node was not found, return false
deleted = false
return deleted
}
deleteAtTail() {
// check for the case when linked list is empty
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return this
}
//if linked list is not empty, get the pointer to first node
let firstNode = this.head
//check for the corner case when linked list has only one element
if (firstNode.nextElement == null) {
this.deleteAtHead()
return this
}
//otherwise traverse to reach second last node
while (firstNode.nextElement.nextElement != null) {
firstNode = firstNode.nextElement
}
//since you have reached second last node, just update its nextElement pointer to point at null, skipping the last node
firstNode.nextElement = null
return this
}
}
/Access HeadNode => list.getHead()
//Set the value of HeadNode => list.getHead()
//Check if list is empty => list.isEmpty()
//Insert at head => list.insertAtHead(value)
//Delete at head => list.deleteAtHead()
//Insert at tail => list.insertAtTail(value)
//Search for element => list.search(value)
//Delete by value => list.deleteVal(value)
//Node class { data Node nextElement}
reverse(list) => {
let previousNode = null
let currentNode = list.getHead() // The current node
let nextNode = null // The next node in the list
//Reversal
while (currentNode != null) {
nextNode = currentNode.nextElement //stores the current node's nextElement in next
currentNode.nextElement = previousNode // Set current node's nextElement to previous
previousNode = currentNode // Make the current node the new previous for the next iteration
currentNode = nextNode // Use next to go to the next node
}
//Set the last element as the new head node
list.setHead(previousNode)
}
let list = new LinkedList()
list.insertAtHead(4)
list.insertAtHead(9)
list.insertAtHead(6)
list.insertAtHead(1)
list.insertAtHead(0)
list.printList()
reverse(list)
list.printList()
In the above program, first, we iterate through the loop and keep adding elements into the linked list and make it reverse. As you can see the loop is running only once, so the program completes in O(n).
Tree
1. Find the minimum value from a Binary Search Tree (BST)
Input: a root node for a binary search tree
bst = {
6 -> 4, 9 //parent -> leftChild, rightChild
4 -> 2, 5
9 -> 8, 12
12 -> 10, 14
}
Output: 2
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value
this.leftChild = null
this.rightChild = null
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(rootValue) {
this.root = new Node(rootValue)
}
insert(currentNode, newValue) {
if (currentNode === null) {
currentNode = new Node(newValue)
} else if (newValue < currentNode.val) {
currentNode.leftChild = this.insert(currentNode.leftChild, newValue)
} else {
currentNode.rightChild = this.insert(currentNode.rightChild, newValue)
}
return currentNode
}
insertBST(newValue) {
if(this.root==null){
this.root=new Node(newValue)
return
}
this.insert(this.root, newValue)
}
preOrderPrint(currentNode) {
if (currentNode !== null) {
console.log(currentNode.val)
this.preOrderPrint(currentNode.leftChild)
this.preOrderPrint(currentNode.rightChild)
}
}
inOrderPrint(currentNode) {
if (currentNode !== null) {
this.inOrderPrint(currentNode.leftChild)
console.log(currentNode.val)
this.inOrderPrint(currentNode.rightChild)
}
}
postOrderPrint(currentNode) {
if (currentNode !== null) {
this.postOrderPrint(currentNode.leftChild)
this.postOrderPrint(currentNode.rightChild)
console.log(currentNode.val)
}
}
search(currentNode, value) {
if (currentNode !== null) {
if (value == currentNode.val) {
return currentNode
} else if (value < currentNode.val) {
return this.search(currentNode.leftChild, value)
} else {
return this.search(currentNode.rightChild, value)
}
} else {
return null
}
}
searchBST(value) {
return this.search(this.root, value)
}
delete(currentNode, value) {
if (currentNode == null) {
return false
}
let parentNode
while (currentNode && (currentNode.val != value)) {
parentNode = currentNode
if (value < currentNode.val) {
currentNode = currentNode.leftChild
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.rightChild
}
}
if (currentNode === null) {
return false
} else if (currentNode.leftChild == null && currentNode.rightChild == null) {
if(currentNode.val==this.root.val){
this.root=null
return true
}
else if (currentNode.val < parentNode.val) {
parentNode.leftChild = null
return true
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = null
return true
}
} else if (currentNode.rightChild == null) {
if(currentNode.val==this.root.val){
this.root=currentNode.leftChild
return true
}
else if (currentNode.leftChild.val < parentNode.val) {
parentNode.leftChild = currentNode.leftChild
return true
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = currentNode.leftChild
return true
}
} else if (currentNode.leftChild == null) {
if(currentNode.val==this.root.val){
this.root = currentNode.rightChild
return true
}
else if (currentNode.rightChild.val < parentNode.val) {
parentNode.leftChild = currentNode.rightChild
return true
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = currentNode.rightChild
return true
}
} else {
let minRight = currentNode.rightChild
while (minRight.leftChild !== null) {
minRight = minRight.leftChild
}
let temp=minRight.val
this.delete(this.root, minRight.val)
currentNode.val = temp
return true
}
}
}
findMin(rootNode) => {
if(rootNode == null)
return null
else if(rootNode.leftChild == null)
return rootNode.val
else
return findMin(rootNode.leftChild)
}
let BST = new BinarySearchTree(6)
BST.insertBST(20)
BST.insertBST(-1)
console.log(findMin(BST.root))
This program begins by checking if the root of BST is null or not. If not null then moves to the left side of a tree and continue checking until you can react at the end. So, then you'll get the smallest number.
Graph
1. Remove Edge
Implement the program to take a graph data that includes source and destination. It should also detect if there's an edge between them or not.
Input: A graph, a source, and a destination
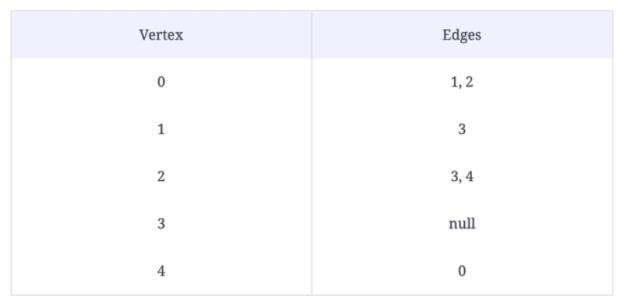
Output: A graph with the edge between the source and the destination removed.
removeEdge(graph, 2, 3)
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data
this.nextElement = null
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
//Insertion At Head
insertAtHead(newData) {
let tempNode = new Node(newData);
tempNode.nextElement = this.head;
this.head = tempNode;
return this; //returning the updated list
}
isEmpty() {
return (this.head == null);
}
//function to print the linked list
printList() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Empty List");
return false;
} else {
let temp = this.head;
while (temp != null) {
process.stdout.write(String(temp.data));
process.stdout.write(" -> ");
temp = temp.nextElement;
}
console.log("null");
return true;
}
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
setHead(newHead) {
this.head = newHead;
return this;
}
getListStr() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Empty List");
return "null";
} else {
let st = "";
let temp = this.head
while (temp != null) {
st += String(temp.data);
st += " -> ";
temp = temp.nextElement;
}
st += "null";
return st;
}
}
insertAtTail(newData) {
//Creating a new Node with data as newData
let node = new Node(newData);
//check for case when list is empty
if (this.isEmpty()) {
//Needs to Insert the new node at Head
this.head = node;
return this;
}
//Start from head
let currentNode = this.head;
//Iterate to the last element
while (currentNode.nextElement != null) {
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement;
}
//Make new node the nextElement of last node of list
currentNode.nextElement = node;
return this;
}
search(value) {
//Start from the first element
let currentNode = this.head;
//Traverse the list until you find the value or reach the end
while (currentNode != null) {
if (currentNode.data == value) {
return true; //value found
}
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement
}
return false; //value not found
}
deleteAtHead() {
//if list is empty, do nothing
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
//Get the head and first element of the list
let firstElement = this.head;
//If list is not empty, link head to the nextElement of firstElement
this.head = firstElement.nextElement;
return this;
}
deleteVal(value) {
let deleted = null; //True or False
//Write code here
//if list is empty return false
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
//else get pointer to head
let currentNode = this.head;
// if first node's is the node to be deleted, delete it and return true
if (currentNode.data == value) {
this.head = currentNode.nextElement;
return true;
}
// else traverse the list
while (currentNode.nextElement != null) {
// if a node whose next node has the value as data, is found, delete it from the list and return true
if (currentNode.nextElement.data == value) {
currentNode.nextElement = currentNode.nextElement.nextElement;
return true;
}
currentNode = currentNode.nextElement;
}
//else node was not found, return false
deleted = false;
return deleted;
}
deleteAtTail() {
// check for the case when linked list is empty
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
//if linked list is not empty, get the pointer to first node
let firstNode = this.head;
//check for the corner case when linked list has only one element
if (firstNode.nextElement == null) {
this.deleteAtHead();
return this;
}
//otherwise traverse to reach second last node
while (firstNode.nextElement.nextElement != null) {
firstNode = firstNode.nextElement;
}
//since you have reached second last node, just update its nextElement pointer to point at null, skipping the last node
firstNode.nextElement = null;
return this;
}
}
class Graph {
constructor(vertices) {
this.vertices = vertices
this.list = []
let it
for (it = 0; it < vertices; it++) {
let temp = new LinkedList()
this.list.push(temp)
}
}
addEdge(source, destination) {
if (source < this.vertices && destination < this.vertices)
this.list[source].insertAtHead(destination)
return this
}
printGraph() {
console.log(">>Adjacency List of Directed Graph<<")
let i
for (i = 0; i < this.list.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write("|" + String(i) + "| => ")
let temp = this.list[i].getHead()
while (temp != null) {
process.stdout.write("[" + String(temp.data) + "] -> ")
temp = temp.nextElement
}
console.log("null ")
}
}
strGraph() {
let str = ""
let i
for (i = 0; i < this.list.length; i++) {
str = str + "|" + String(i) + "| => "
let temp = this.list[i].getHead()
while (temp != null) {
str += ("[" + String(temp.data) + "] -> ")
temp = temp.nextElement
}
str += "null "
}
return str
}
}
removeEdge(graph, source, dest) => {
if(graph.list.length == 0){
return graph
}
if(source >= graph.list.length || source < 0){
return graph
}
if(dest >= graph.list.length || dest < 0){
return graph
}
graph.list[source].deleteVal(dest)
return graph
}
let g = new Graph(5)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 4)
g.addEdge(4, 0)
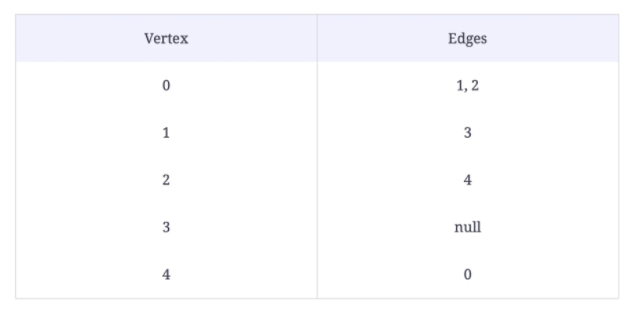
console.log("Before removing edge")
g.printGraph()
removeEdge(g, 1, 3)
console.log("\nAfter removing edge")
g.printGraph()
In this solution we use indexing and deletion. Hope you checked the solution. Since we store graph vertices in an array we can access the source linked list. then you just need to call delete function for linked lists to remove the edges. The time complexity of this program is O(E), here E denotes traversed edges.
Hash Table
1. Convert Max-Heap to Min-Heap
You need to write a program that will convert a binary max-heap into a binary min-heap.
Input: a Max-Heap [9,4,7,1,-2,6,5]
Output: [-2,1,5,9,4,6,7]
minHeapify(heap, index) => {
let left = index * 2
let right = (index * 2) + 1
let smallest = index
if ((heap.length > left) && (heap[smallest] > heap[left])) {
smallest = left
}
if ((heap.length > right) && (heap[smallest] > heap[right]))
smallest = right
if (smallest != index) {
let tmp = heap[smallest]
heap[smallest] = heap[index]
heap[index] = tmp
minHeapify(heap, smallest)
}
return heap
}
convertMax(maxHeap) => {
for (let i = Math.floor((maxHeap.length) / 2); i > -1; i--)
maxHeap = minHeapify(maxHeap, i)
return maxHeap
}
let maxHeap = [9,4,7,1,-2,6,5]
console.log(convertMax(maxHeap))
Here we consider maxHeap as an array and we did array hash operations on it. You can see this in the above program. So, the time complexity of this program is O(nlog(n))O(nlog(n)).
That's it!
You can find some program a bit difficult at the beginning but once you know the logic you can write easily. Thank you for reading.
If you love this article, you can buy me a coffee: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/harry1408
Comments
Loading comments…