
Declaring variables is always a hectic task for programmers. And as the program increases in size, the pain increases too. At the beginning of the code, we try to declare variables with a valid name like temp, hashedKey, and likewise. But as time goes on, our code will be huge and we will be exhausted of the thinking capacity to find a suitable variable name. Then we name them x, y, and so on.
The problem becomes more complicated when you need to declare variables dynamically in a loop. I came up with three ways to do this in Python.
1. Using the exec command
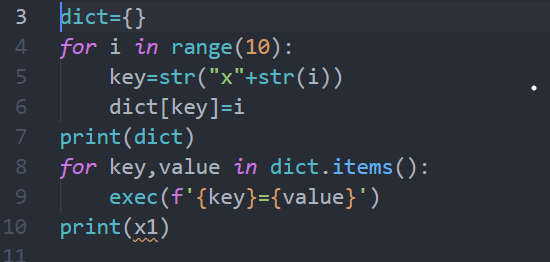
In the above program, I initially declared an empty dictionary and added the elements into the dictionary. I used string concatenation method to declare dynamic variables like x1, x2, x3……. . Then I assumed the values from the for loop to the dynamic variables. The dictionary will look like
{‘x0’: 0, ‘x1’: 1, ‘x2’: 2, ‘x3’: 3, ‘x4’: 4, ‘x5’: 5, ‘x6’: 6, ‘x7’: 7, ‘x8’: 8, ‘x9’: 9}
You can learn about dictionaries here. Python Dictionaries
Finally, I iterated over the dictionary and separated the keys into a standalone variable using the exec command. The exec command executes the Python code inside it. exec( f ‘ {key}={value}’) — here f represents the string format.
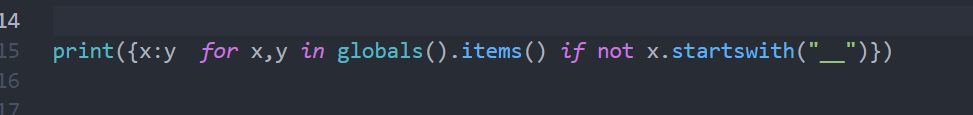
Now you can check the global variables using the above code and you can see that the dictionary keys are now copied as standalone global variables. The output will be like this. You can clearly see that there are 10 variables declared starting from x0 to x9.
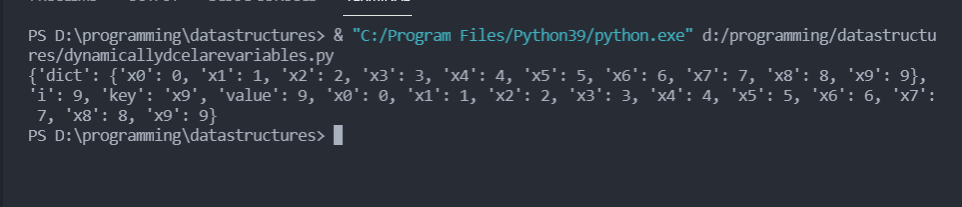
Note: The dictionary remains unchanged.
2. Using globals()
globals() function in Python returns the dictionary of the current global symbol table. It requires no params. It also returns the global variables declared inside a program.
You can learn about globals() here.
Code
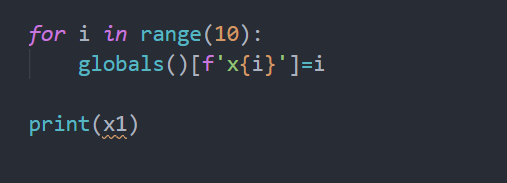
globals() is a dictionary which contains all the global variables with the variable name as its key and value as its value. Declaring variables using globals is the same as declaration using a dictionary. The output is the same as the first one.
3. Using OOP
One of the greatest features of Python is its support for OOP (Object-Oriented Programming). We shall get to the use of that amazing property to declare variables dynamically.
Code
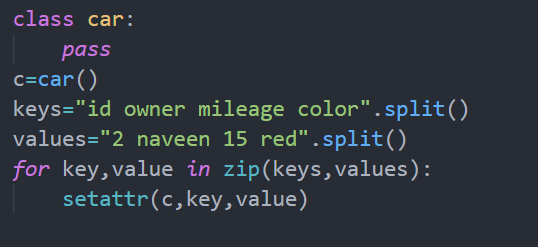
I think most of you are familiar with classes and the zip method. But for those who have not explored it, you can learn from here. Python zip() Python Oops Concept
In the above code, I have dynamically declared the attributes of an object instead of declaring it as a global variable. The set attribute is a class method which enables us to declare new attributes to an object after it has been initialized and not for the whole class.
You can check the attributes of the object using the below command.
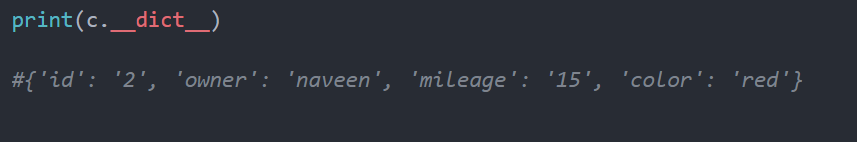
Thanks to everyone who contributed to this article. How can you dynamically create variables via a while loop?
Thank you everyone for reading.
If you want me to post any other articles on any topic, feel free to ping me on WhatsApp +91 8870499146.
Comments
Loading comments…