The AWS Load Balancer Controller manages AWS Elastic Load Balancers for a Kubernetes cluster.

What is the AWS Load Balancer controller?
The AWS Load Balancer Controller manages AWS Elastic Load Balancers for a Kubernetes cluster. The controller provisions the following resources:
- It satisfies Kubernetes Ingress resources by provisioning Application Load Balancers.
- It satisfies Kubernetes Service resources by provisioning Network Load Balancers.
Let’s Deploy…
Prerequisites
- AWS IAM access with admin privileges
- AWS EKS cluster (1.22)
- AWS CLI
Step 1: Setup permissions in IAM
1.1 Create an IAM policy
- Download the below-given IAM policy for the AWS Load Balancer Controller.
curl -o iam_policy.json [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.4.3/docs/install/iam_policy.json](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.4.3/docs/install/iam_policy.json)
- Create an IAM policy using the policy downloaded in the previous step.
aws iam create-policy \
--policy-name AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy \
--policy-document file://iam_policy.json
1.2 Create an IAM role
- We need to create an IAM role and attach the above-created IAM policy. You can use the AWS CLI to create the IAM role.
- View your cluster’s OIDC provider URL.
aws eks describe-cluster --name my-cluster --query "cluster.identity.oidc.issuer" --output text
- The example output is as follows.
oidc.eks._region-code_.amazonaws.com/id/_EXAMPLED539D4633E53DE1B71EXAMPLE_
- Copy the following contents to your device. Replace
_111122223333_with your account ID. Replace_region-code_with the AWS Region that your cluster is in. Replace_EXAMPLED539D4633E53DE1B71EXAMPLE_with the output returned in the previous step. After replacing the text, run the modified command to create theload-balancer-role-trust-policy.jsonfile.
cat >load-balancer-role-trust-policy.json <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.region-code.amazonaws.com/id/EXAMPLED539D4633E53DE1B71EXAMPLE"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"oidc.eks.region-code.amazonaws.com/id/EXAMPLED539D4633E53DE1B71EXAMPLE:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com",
"oidc.eks.region-code.amazonaws.com/id/EXAMPLED539D4633E53DE1B71EXAMPLE:sub": "system:serviceaccount:kube-system:aws-load-balancer-controller"
}
}
}
]
}
EOF
- Create the IAM role.
aws iam create-role \
--role-name AmazonEKSLoadBalancerControllerRole \
--assume-role-policy-document file://"load-balancer-role-trust-policy.json"
- Attach the required Amazon EKS-managed IAM policy to the IAM role. Replace
_111122223333_with your account ID.
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::111122223333:policy/AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy \
--role-name AmazonEKSLoadBalancerControllerRole
Step 2: Installing the AWS load balancer controller add-on
2.1 Add the Service Account
- Replace
_111122223333_with your account ID. After replacing the text, run the modified command to create theaws-load-balancer-controller-service-account.yamlfile.
cat >aws-load-balancer-controller-service-account.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/name: aws-load-balancer-controller
name: aws-load-balancer-controller
namespace: kube-system
annotations:
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/AmazonEKSLoadBalancerControllerRole
EOF
- Create the Kubernetes service account on your cluster. The Kubernetes service account named
aws-load-balancer-controlleris annotated with the IAM role that you created named_AmazonEKSLoadBalancerControllerRole_. - For the kubectl authentication you need the kubeconfig file, Run the update-kubeconfig command and confirm that it updates the config file under ~/.kube/config:
aws eks --region region-code update-kubeconfig --name cluster_name
- Execute the below given kubectl command to configure the service account.
kubectl apply -f aws-load-balancer-controller-service-account.yaml
2.2 Install the AWS Load Balancer Controller using Helm V3
- Add the
eks-chartsrepository.
helm repo add eks [https://aws.github.io/eks-charts](https://aws.github.io/eks-charts)
- Run the update
helm repo update
- Replace
_my-cluster_with your own. The following commandaws-load-balancer-controlleris the Kubernetes service account you created in a previous step.
helm install aws-load-balancer-controller eks/aws-load-balancer-controller \
-n kube-system \
--set clusterName=my-cluster \
--set serviceAccount.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.name=aws-load-balancer-controller
- Verify the deployment
kubectl get deployment -n kube-system aws-load-balancer-controller
Step 3: Configuration of ingress routes
3.1 Deploy a sample application
- Deploy a sample application to configure ingress routes, Here we are deploying the Nginx image in the default namespace and exposing it as ClusterIP
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
##SVC Exposing as clusterIP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: nginx
- Execute the below given kubectl commands to deploy a sample application
kubectl apply -f nginx_deploy.ymlkubectl get deployment nginx
3.2 Add ingress route
- To customize their behavior, you can add annotations to Kubernetes Ingress and Service objects.
- Add two public subnets in the “alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/subnets”
- We’ll use the “alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.${action-name}” annotation to setup an ingress to redirect HTTP traffic into HTTPS
- Here we’ll be using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM )for configuring HTTPS, You need to provide the ACM arn in the “alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn”
- Replace the host value with your desired custom domain and service name example with SVC that you created during the sample application deployment.
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
namespace: default
name: ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/subnets: public_subnet_one,public_subnet_two
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: acm_ssl_arn
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.name: app
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: >-
{
"Type": "redirect",
"RedirectConfig": {
"Protocol": "HTTPS",
"Port": "443",
"Host": "#{host}",
"Path": "/#{path}",
"Query": "#{query}",
"StatusCode": "HTTP_301"
}
}
spec:
rules:
- host: app.example.com ##Replace the host value with your desired custom domain
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ssl-redirect
port:
name: use-annotation
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: example ##Replace service name example with SVC that you created during the sample application deployment
port:
number: 80 ##Replace 80 with application port number
kubectl apply -f ingress.ymlError from server (InternalError): error when creating "ingress.yml": Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "vingress.elbv2.k8s.aws": Post "[https://aws-load-balancer-webhook-service.kube-system.svc:443/validate-networking-v1-ingress?timeout=10s](https://aws-load-balancer-webhook-service.kube-system.svc/validate-networking-v1-ingress?timeout=10s)": context deadline exceeded
oops !! I think we have got a problem here
- The above error indicates that the k8s control plane is not able to connect to the AWS-load-balancer-controller pods running on the worker nodes
- For the AWS lb controller, We need to allow port 9443 for webhook access.
- So add port 9443 in the worker nodes security group to allow access from the control plane to the webhook port of the AWS load balancer controller.

- Let’s run the kubectl command again.
- Now, let's check if the load balancer is created or not
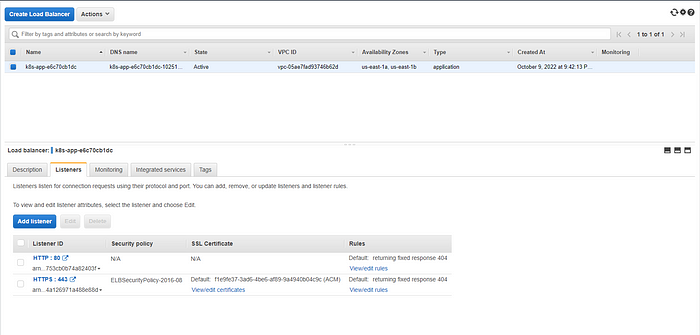
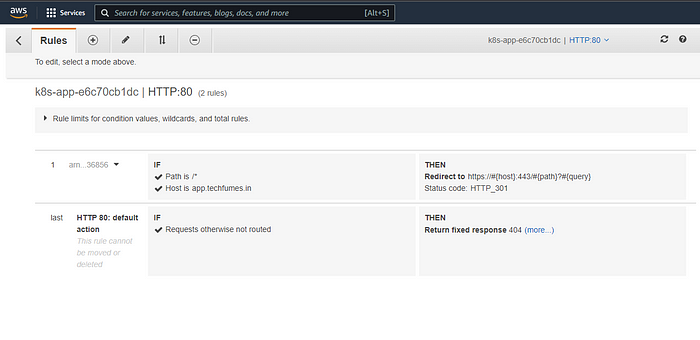
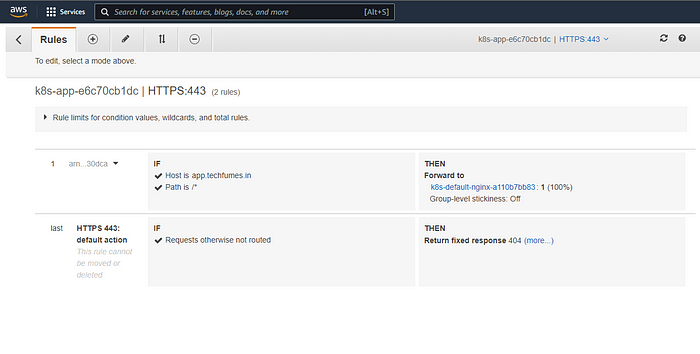
- The load balancer and rules are created, Now let’s try accessing the sample application using the hostname that we added in the ingress configuration.
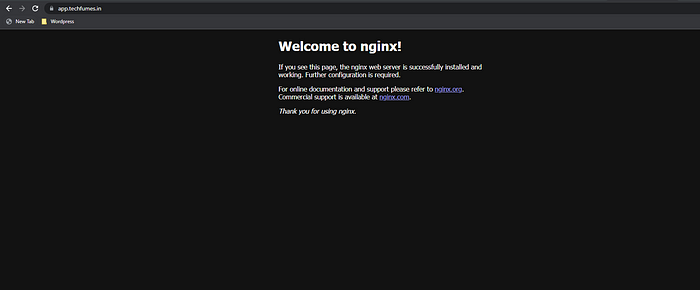
- We can access the sample application(Nginx) using the hostname and thus verify that we have successfully configured the AWS load balancer controller and Ingress routes.
References
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/aws-load-balancer-controller.html
- https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.4/
- https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-load-balancer-controller/issues/2462
- https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-load-balancer-controller/blob/main/docs/guide/ingress/annotations.md
Comments
Loading comments…